FTTH Butterfly Optic Cables: A Comprehensive Guide

In the ever - evolving landscape of modern communication, the demand for high - speed, reliable internet connections has reached unprecedented levels. Fiber - to - the - Home (FTTH) technology has emerged as a frontrunner in meeting this demand, and at the heart of many FTTH installations lies the butterfly optic cable. This article delves deep into the world of FTTH butterfly optic cables, exploring their design, applications, installation process, and much more.
What are FTTH Butterfly Optic Cables?
Definition and Naming
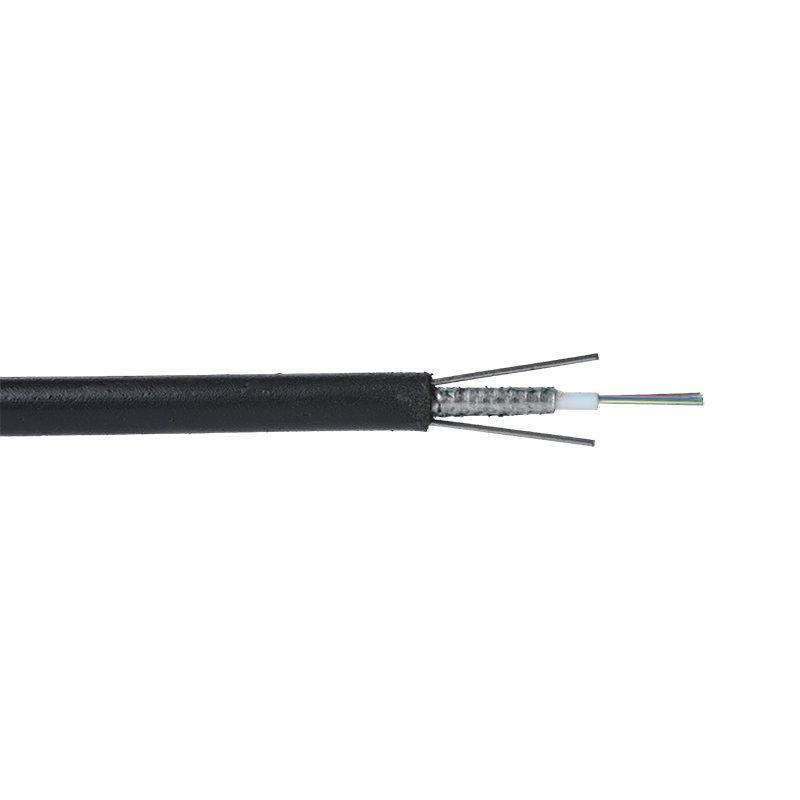
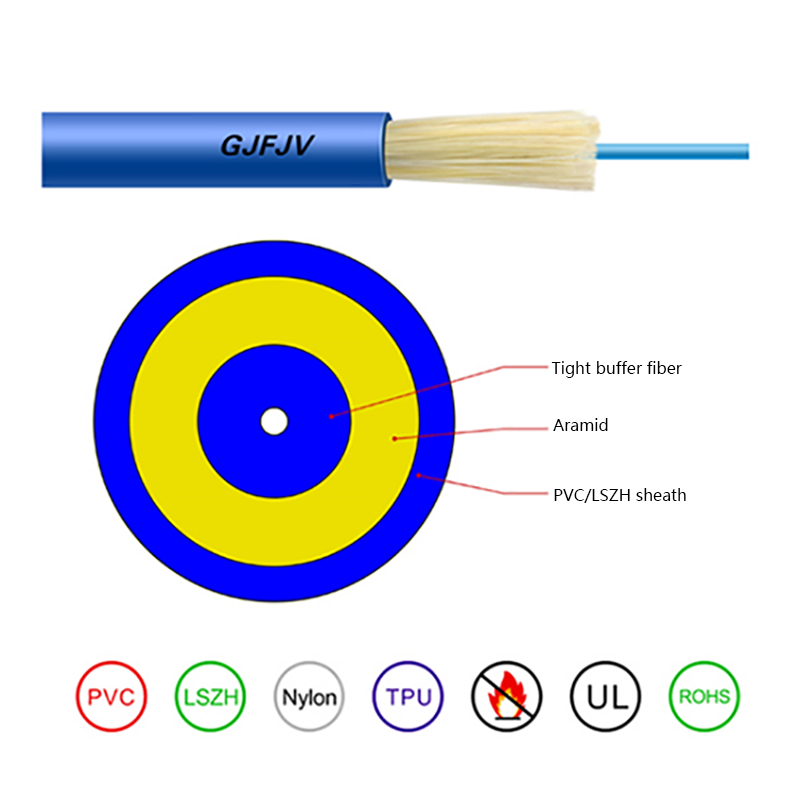
As the name suggests, FTTH butterfly optic cables are so - named due to their cross - sectional shape, which resembles the wings of a butterfly. These cables are a type of fiber optic cable specifically designed for use in FTTH networks, where they play a crucial role in delivering high - speed optical signals directly to the end - user's premises.
Structure and Components
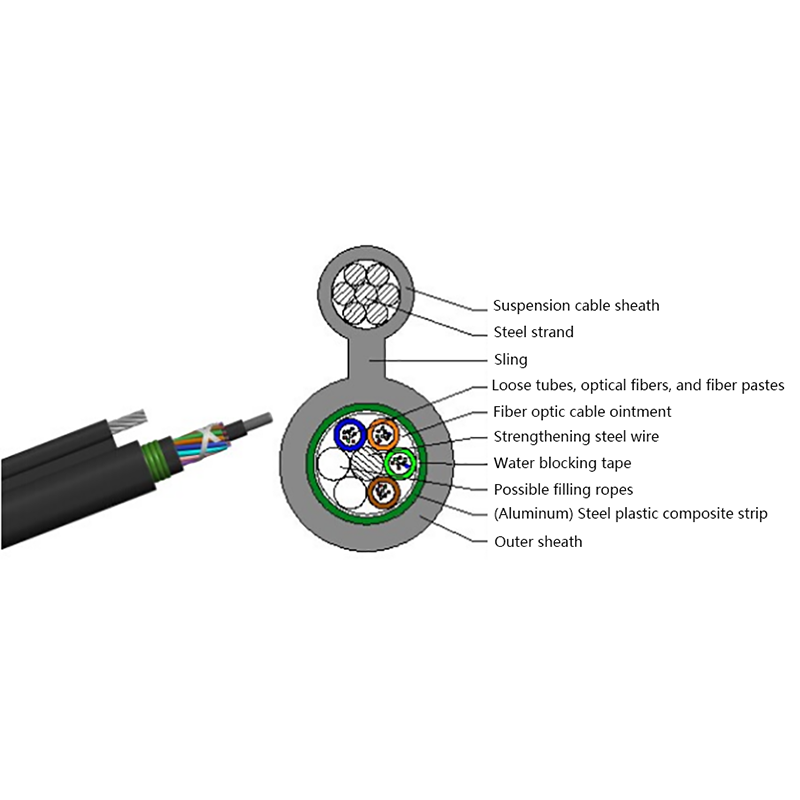
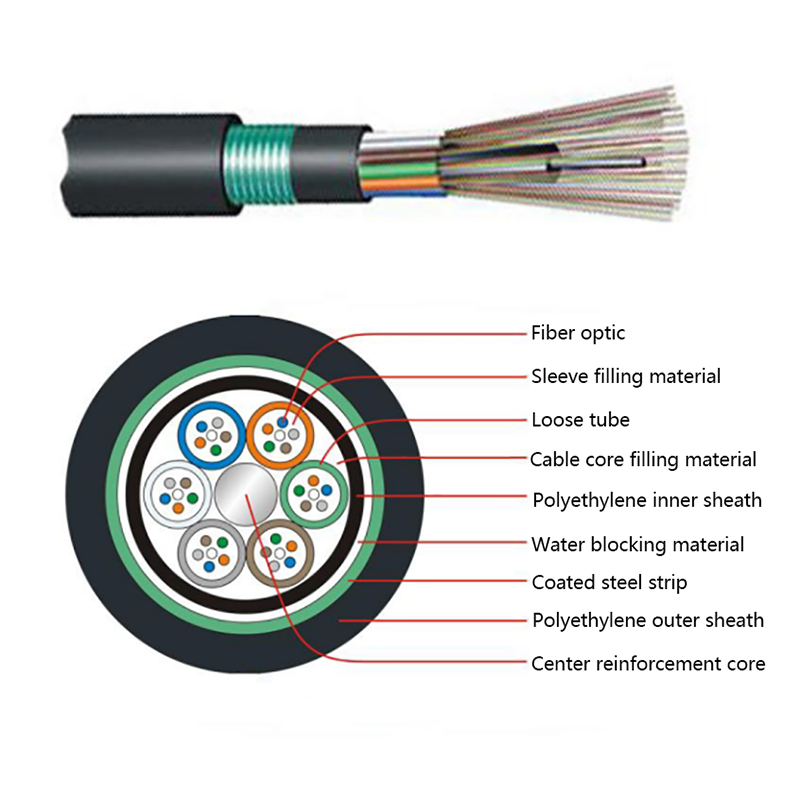
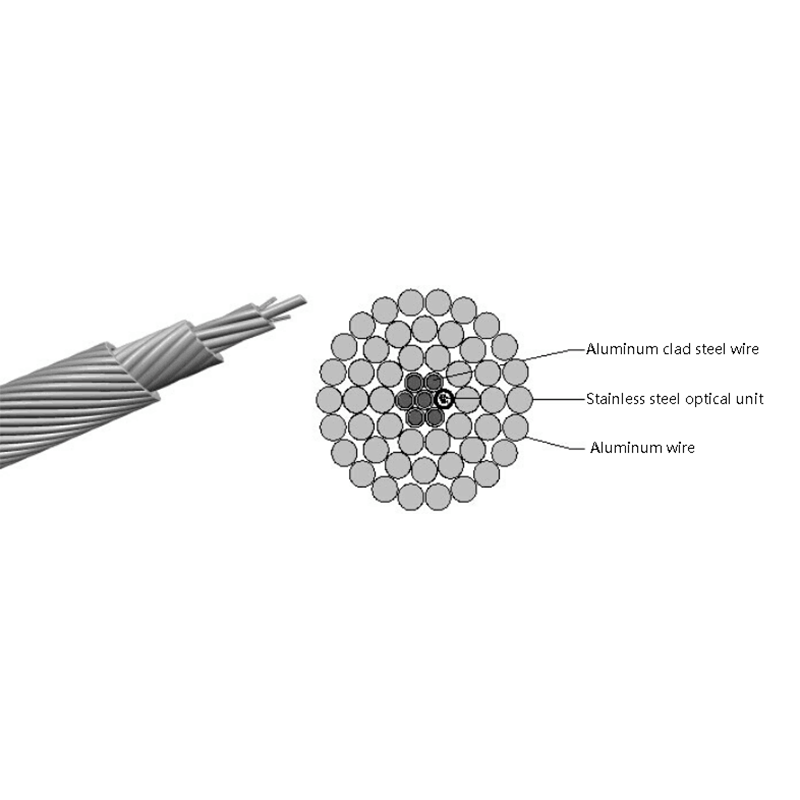
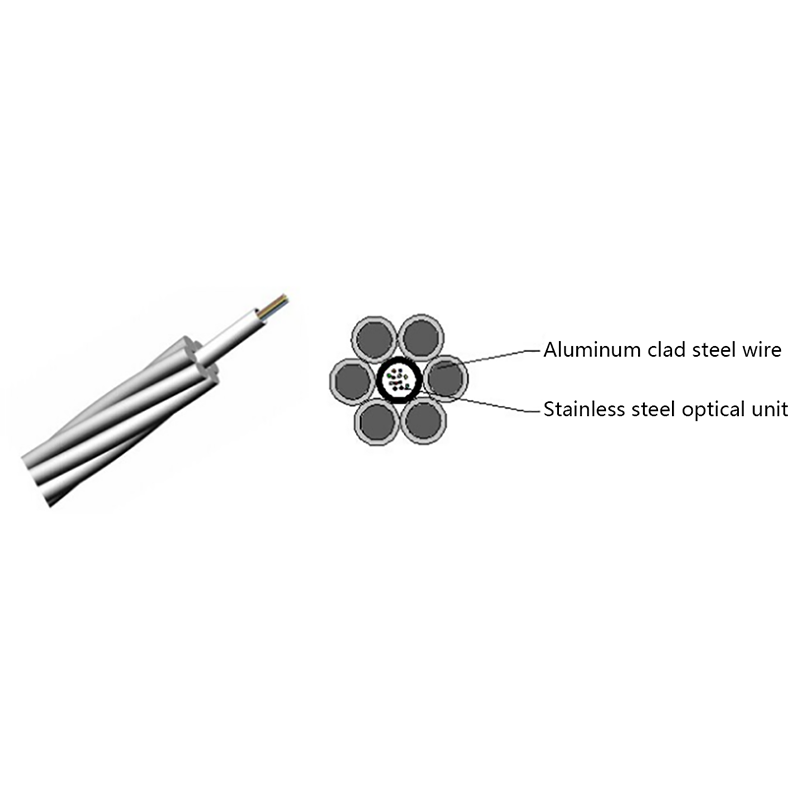
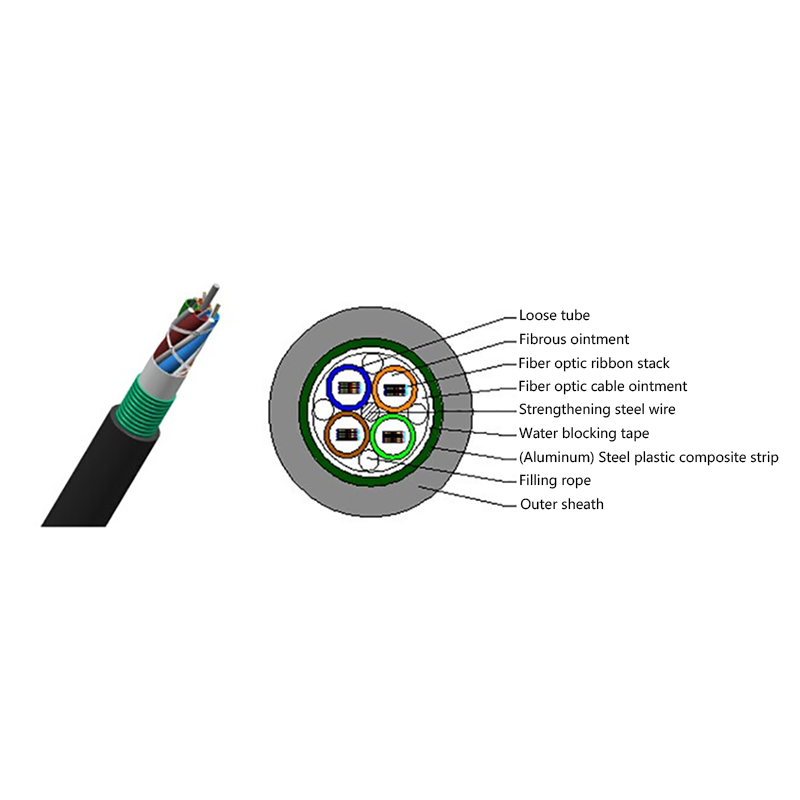
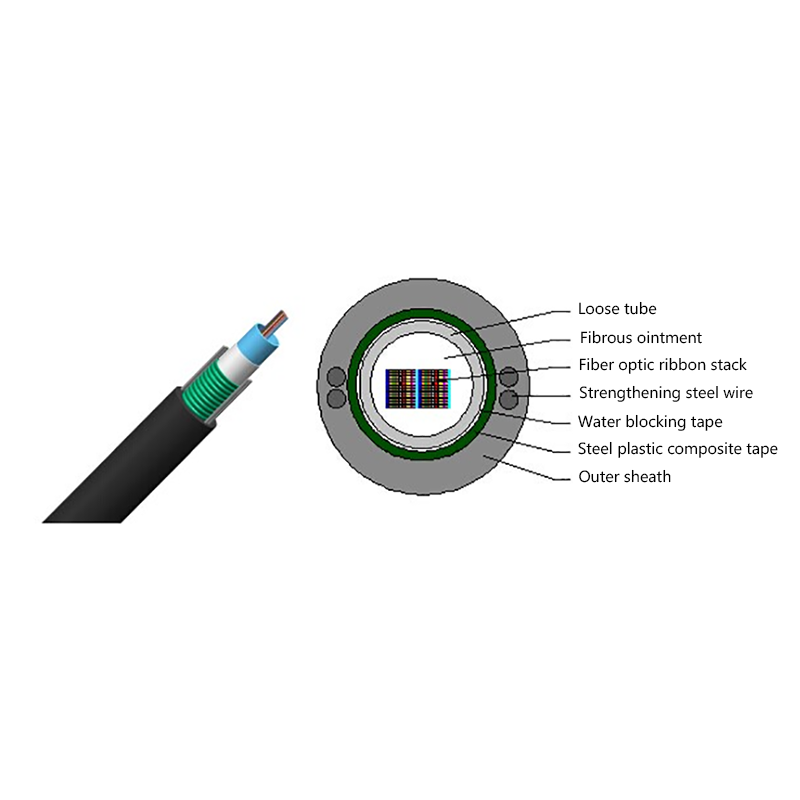
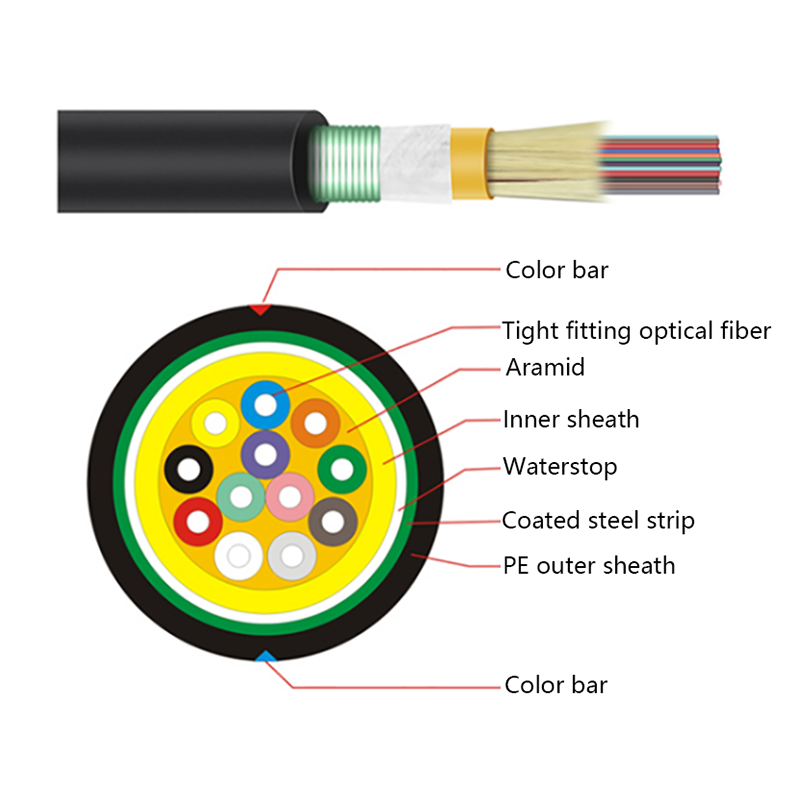
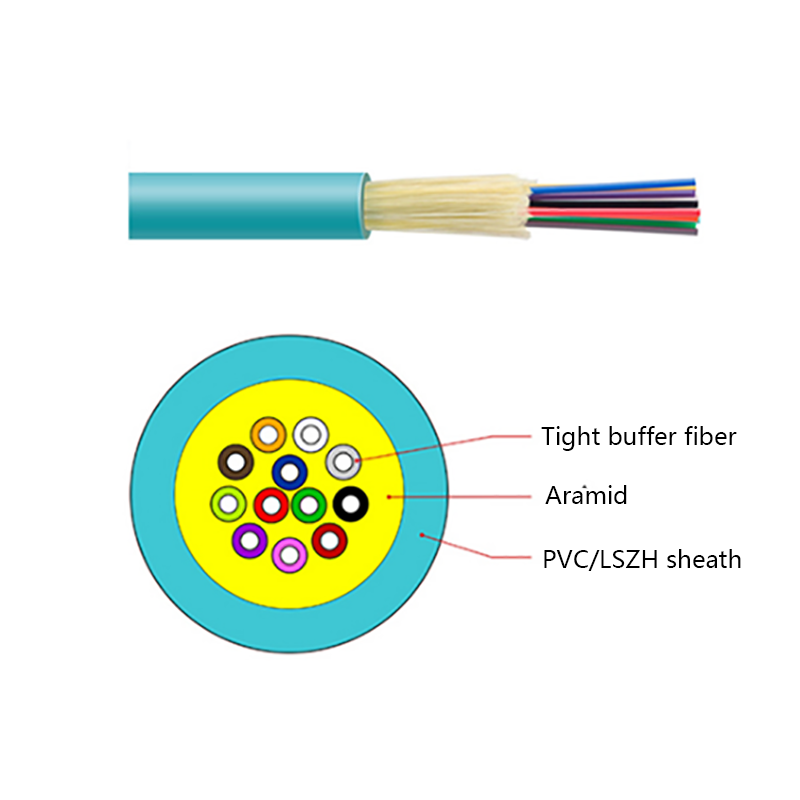
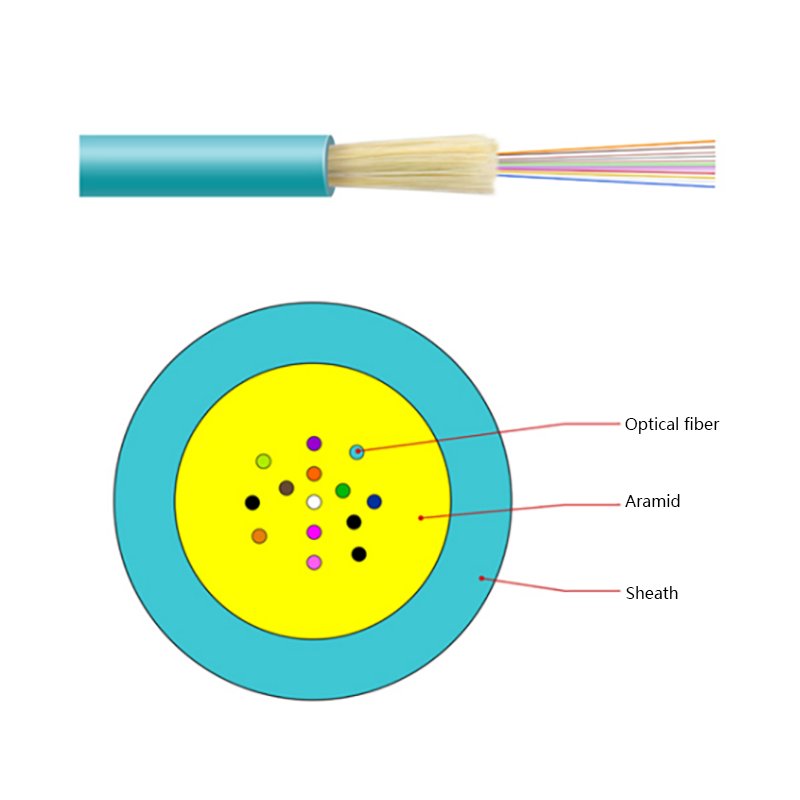
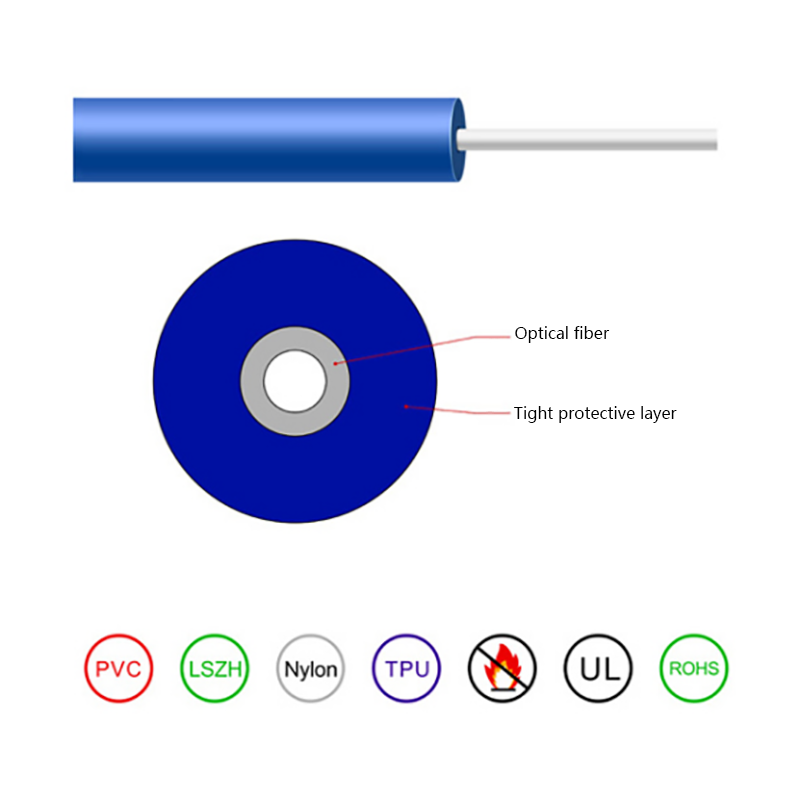
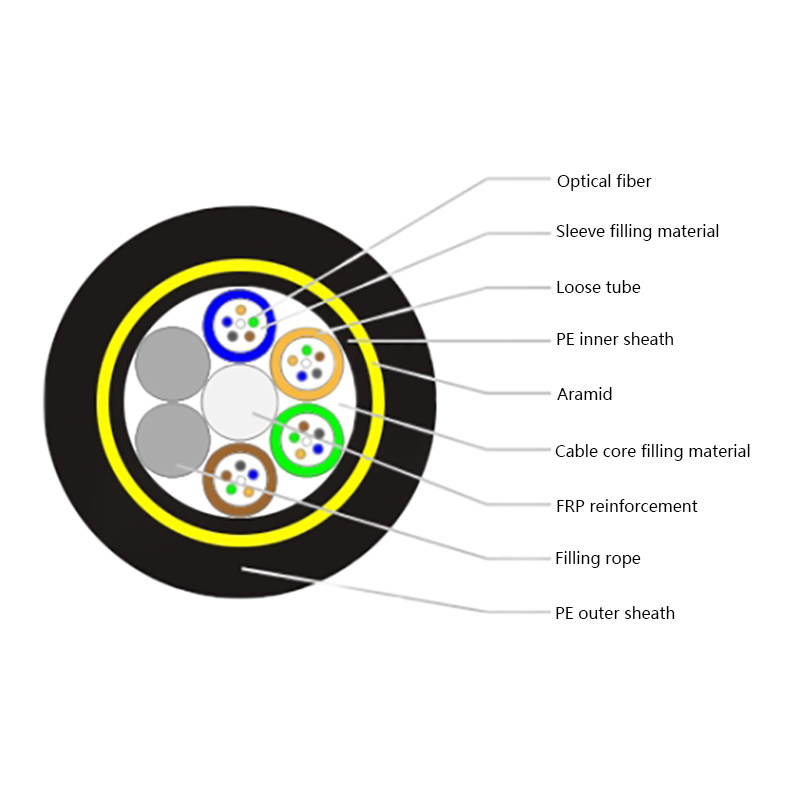
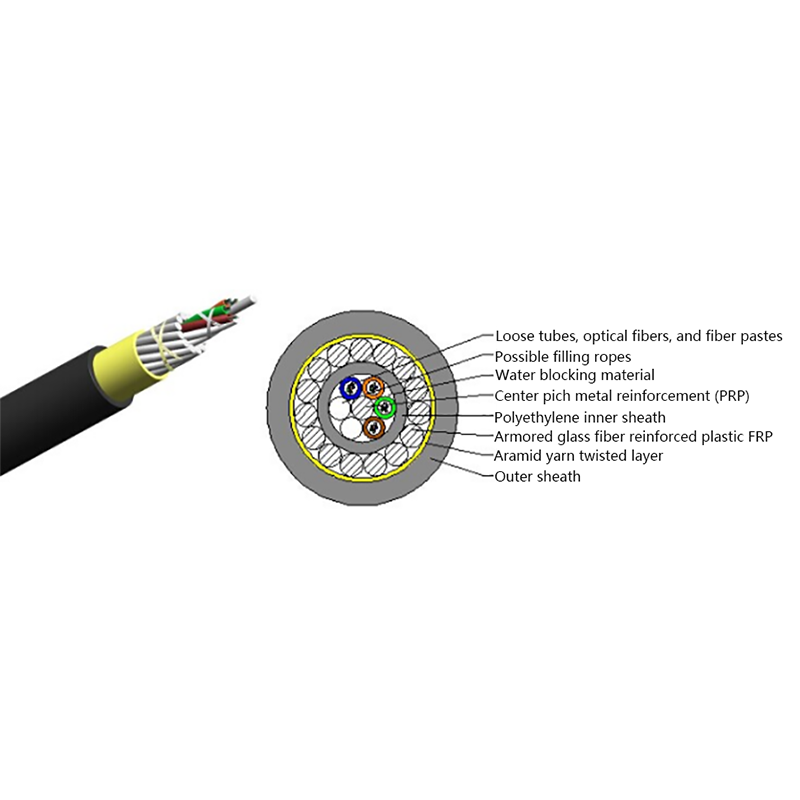
Fiber Core: At the center of the butterfly optic cable is the fiber core, which is responsible for transmitting light signals. The fiber core can be either single - mode or multi - mode. Single - mode fibers are typically used for long - distance and high - bandwidth applications, as they can carry light signals over much longer distances with less attenuation. Multi - mode fibers, on the other hand, are more suitable for shorter - distance applications within a building or campus, as they can carry multiple light signals simultaneously, allowing for higher data transfer rates over shorter spans.
Strength Members: To ensure the cable can withstand the mechanical stresses during installation and in its operational environment, butterfly optic cables are equipped with strength members. These are usually made of materials such as steel wire or fiberglass - reinforced plastic (FRP). Steel wire provides high tensile strength, making it suitable for applications where the cable may be subjected to significant pulling forces. FRP, on the other hand, is lighter in weight and offers good resistance to corrosion and electromagnetic interference, making it a popular choice for indoor and environmentally - sensitive installations.
Outer Jacket: The outer jacket of the butterfly optic cable serves as a protective layer, shielding the fiber core and strength members from external factors such as moisture, abrasion, and physical damage. The jacket is often made of materials with properties such as low - smoke zero - halogen (LSZH), which is important for fire - safety in indoor environments. LSZH - coated cables produce less smoke and no harmful halogen - based gases when exposed to fire, reducing the risk of toxicity and improving visibility during emergency situations.
Features and Advantages of Butterfly Optic Cables
Space - Saving Design
One of the most significant advantages of butterfly optic cables is their flat and compact design. The cross - sectional shape of the cable, similar to that of a butterfly's wings, allows it to occupy minimal space. This makes it ideal for installations in areas with limited space, such as inside walls, along baseboards, or in conduits with tight diameters. In residential homes, for example, the flat profile of the cable can be easily routed along the edges of rooms or hidden behind furniture, providing a discreet and unobtrusive solution for bringing high - speed internet access.
Flexibility and Bendability
Butterfly optic cables are highly flexible and can be bent around corners and obstacles with relative ease. This flexibility is crucial for installations where the cable needs to navigate through complex building structures or around existing infrastructure. The ability to bend the cable without causing damage to the fiber core ensures that the optical signal transmission remains stable. In fact, modern butterfly optic cables are designed to withstand a certain degree of bending without significant attenuation of the signal. For instance, some cables can be bent to a radius as small as 20 - 30 mm without affecting the performance, making them suitable for applications where tight bends are required.
Ease of Installation
The design of butterfly optic cables also contributes to their ease of installation. The flat shape of the cable allows for simple and straightforward routing. Installation technicians can use specialized tools, such as cable staples or clips, to secure the cable to surfaces. The cable can be easily stapled to wooden studs in a wall or clipped to cable trays in a ceiling. Additionally, the lightweight nature of the cable makes it easier to handle during installation, reducing the physical strain on the installers. In comparison to traditional round - shaped fiber optic cables, which may require more complex installation techniques and tools, butterfly optic cables offer a more streamlined installation process.
Cost - Effectiveness
In terms of cost, butterfly optic cables can be a cost - effective solution for FTTH installations. Their simple structure and lightweight design contribute to lower material costs. Additionally, the ease of installation reduces labor costs, as less time and effort are required to install the cable compared to other types of fiber optic cables. The cost - effectiveness of butterfly optic cables makes them an attractive option for both large - scale FTTH deployments by service providers and for individual homeowners looking to upgrade their internet connectivity.
Applications of FTTH Butterfly Optic Cables
Residential FTTH Installations
Butterfly optic cables are widely used in residential FTTH installations. In today's digital age, households rely heavily on high - speed internet for activities such as streaming high - definition videos, online gaming, working from home, and smart home device connectivity. Butterfly optic cables can deliver the high - bandwidth requirements needed to support these activities seamlessly. They can be installed from the street cabinet or distribution point to the home, providing a reliable and fast connection. Inside the home, the cable can be routed to various rooms to connect multiple devices, such as smart TVs, computers, and tablets, ensuring that every member of the household can enjoy a high - quality internet experience.
Commercial and Office Buildings
In commercial and office buildings, butterfly optic cables also play a vital role. Offices require high - speed and reliable internet connections to support business operations, including cloud - based services, video conferencing, and large - scale data transfer. Butterfly optic cables can be installed in a building's vertical and horizontal cable runs, connecting different floors and individual offices. The space - saving design of the cable is particularly beneficial in commercial buildings, where space may be at a premium. Additionally, the ability to support high - bandwidth applications makes it suitable for businesses that deal with large amounts of data, such as financial institutions, media companies, and technology startups.
Campus Networks (Schools, Universities)
Campus networks in schools and universities also make use of butterfly optic cables. These institutions need to provide high - speed internet access to multiple buildings, classrooms, dormitories, and administrative offices. Butterfly optic cables can be used to create a robust and reliable network infrastructure across the campus. They can be installed underground or above - ground, depending on the campus layout and requirements. In classrooms, the cable can be used to connect interactive whiteboards, computers, and other educational technology devices, enabling seamless access to online learning resources. In dormitories, students can enjoy high - speed internet for their academic and entertainment needs.
Installation Process of FTTH Butterfly Optic Cables
Pre - installation Planning
Before starting the installation of butterfly optic cables, careful pre - installation planning is essential. This includes assessing the route the cable will take from the source (such as a central distribution point) to the destination (the end - user's premises). The installer needs to consider factors such as the location of existing infrastructure, potential obstacles (such as walls, pipes, and electrical conduits), and the aesthetic requirements of the installation area. A detailed plan should be created, indicating the exact path of the cable, the location of any splices or connections, and the type of installation hardware (such as staples, clips, or conduits) that will be used.
Cable Routing and Fixing
Once the pre - installation planning is complete, the next step is to route the butterfly optic cable along the planned path. The flat shape of the cable allows it to be easily guided through tight spaces. If the installation is indoors, the cable can be routed along walls, ceilings, or baseboards. It can be fixed in place using cable staples or clips at regular intervals. When routing the cable around corners, care should be taken to ensure that the bending radius of the cable is not exceeded. In outdoor installations, the cable may need to be installed in conduits for additional protection. The conduits can be buried underground or installed above - ground, depending on the specific requirements of the installation.
Termination and Connection
After the cable has been routed and fixed, the next step is to terminate the cable and make the necessary connections. Termination involves preparing the end of the cable for connection to the optical network terminal (ONT) or other networking equipment. This typically involves stripping the outer jacket of the cable to expose the fiber core and strength members. Specialized tools are used to strip the cable without damaging the fiber core. Once the cable is stripped, the fiber core is then connected to the ONT or other equipment using techniques such as fusion splicing or mechanical splicing. Fusion splicing involves melting the ends of the fibers together to create a seamless connection, while mechanical splicing uses a mechanical connector to join the fibers. The choice of splicing technique depends on factors such as the type of cable, the installation environment, and the cost and time constraints of the project.
Performance Parameters of FTTH Butterfly Optic Cables
| Parameter | Details |
| Attenuation | For single - mode fibers, at 1310 nm, the attenuation is typically ≤ 0.4 dB/km, and at 1550 nm, it is ≤ 0.3 dB/km. For multi - mode fibers, the attenuation values may vary depending on the type of multi - mode fiber (e.g., OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4). Lower attenuation values are desirable as they allow for longer transmission distances without significant signal degradation. |
| Chromatic Dispersion | In single - mode fibers, at 1550 nm, the chromatic dispersion is usually ≤ 18 ps/nm.km, and at 1625 nm, it is ≤ 22 ps/nm.km. Chromatic dispersion can limit the data - transmission rate over long distances, so minimizing this parameter is important for high - speed applications. |
| Bend Loss | Modern butterfly optic cables are designed to have low bend loss. For example, they can be bent to a radius of 20 - 30 mm with minimal increase in attenuation. Low bend loss ensures that the cable can be installed in areas with tight bends without sacrificing signal quality. |
| Tensile Strength | The tensile strength of the cable depends on the type of strength members used. Cables with steel wire strength members can typically withstand higher tensile forces compared to those with FRP strength members. The tensile strength is specified in Newtons (N), and it indicates the maximum pulling force the cable can endure during installation or in its operational environment without damage to the fiber core. |
Market Trends and Future Outlook
Increasing Demand for High - Speed Internet
With the continuous growth of digital services, such as 4K and 8K video streaming, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR), the demand for high - speed internet is on the rise. FTTH technology, with its ability to provide gigabit - speed connections, is becoming increasingly popular. As a result, the demand for butterfly optic cables, which are a key component of FTTH installations, is also expected to grow. Service providers around the world are investing in expanding their FTTH networks to meet the growing demand for high - speed internet, and this trend is likely to continue in the coming years.
Technological Advancements
The field of fiber optic cable technology is constantly evolving, and butterfly optic cables are no exception. Manufacturers are working on developing cables with even better performance characteristics, such as lower attenuation, higher tensile strength, and improved flexibility. New materials and manufacturing processes are being explored to enhance the quality and reliability of the cables. For example, the development of new types of fiber cores and coatings may lead to cables with reduced signal loss and increased resistance to environmental factors. Additionally, advancements in cable termination and connection techniques are making the installation process even more efficient and reliable.
Competition and Cost - Optimization
As the market for FTTH butterfly optic cables grows, competition among manufacturers is intensifying. This competition is driving manufacturers to optimize costs while maintaining high - quality standards. Manufacturers are looking for ways to reduce production costs through economies of scale, improved manufacturing processes, and the use of more cost - effective materials. At the same time, they are also focusing on innovation to differentiate their products in the market. This competition is ultimately beneficial for consumers and service providers, as it leads to better - quality products at more competitive prices.
Challenges and Solutions in Using FTTH Butterfly Optic Cables
Mechanical Damage
One of the challenges in using butterfly optic cables is the risk of mechanical damage during installation and in the operational environment. The flat shape of the cable, while advantageous in many ways, can make it more vulnerable to certain types of mechanical stress. For example, if the cable is accidentally stepped on or pinched, it can cause damage to the fiber core or the strength members. To mitigate this risk, installers should take care to route the cable in areas where it is less likely to be exposed to mechanical stress. Additionally, protective measures such as installing the cable in conduits or using cable guards can be employed.
Moisture and Environmental Factors
Moisture can also pose a problem for butterfly optic cables. If water penetrates the cable, it can cause corrosion of the strength members and damage to the fiber core, leading to signal degradation. To address this issue, manufacturers design the outer jackets of the cables to be water - resistant. In addition, some cables are filled with a water - blocking compound to prevent the ingress of moisture. For outdoor installations, special consideration should be given to the cable's ability to withstand environmental factors such as extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. Cables with appropriate UV - resistant coatings and temperature - rated materials should be selected for such applications.
Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
Another challenge is ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure. In some cases, when upgrading an existing network to FTTH, the butterfly optic cable may need to be integrated with older types of cables or networking equipment. This can pose compatibility issues, such as differences in cable diameters, connection types, and signal characteristics. To overcome this challenge, installers may need to use adapters or converters to ensure seamless integration. Additionally, careful planning and testing should be carried out before the installation to identify and address any potential compatibility problems.
Conclusion
FTTH butterfly optic cables have emerged as a crucial component in the modern communication infrastructure. Their unique design, with a cross - sectional shape resembling a butterfly's wings, offers numerous advantages such as space - saving, flexibility, ease of installation, and cost - effectiveness. These cables find wide applications in residential, commercial, and campus network settings, enabling the delivery of high - speed, reliable internet connections. As the demand for high - speed internet continues to grow, along with technological advancements in the fiber optic cable industry, the future of FTTH butterfly optic cables looks promising. However, like any technology, they also face challenges such as mechanical damage, moisture, and compatibility issues, which can be addressed through proper installation techniques, material selection, and careful planning. Overall, FTTH butterfly optic cables are set to play a significant role in shaping the future of high - speed communication networks.



 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体