ADSS Cables Explained: Design, Installation, and Real-World Applications
Understanding ADSS Cables in Modern Fiber Optic Networks
ADSS Cables (All-Dielectric Self-Supporting Cables) are a specialized type of fiber optic cable designed for aerial installation without metallic components. Unlike traditional fiber cables that rely on messenger wires or steel reinforcement, ADSS cables are fully dielectric, making them ideal for installation on power transmission lines and utility poles. Their structure allows them to withstand mechanical tension, wind load, and environmental stress while maintaining stable optical performance. As demand for high-speed broadband, FTTH, and long-distance communication grows, ADSS cables have become a preferred solution in telecom and power grid infrastructure.
Core Structure and Materials of ADSS Cables
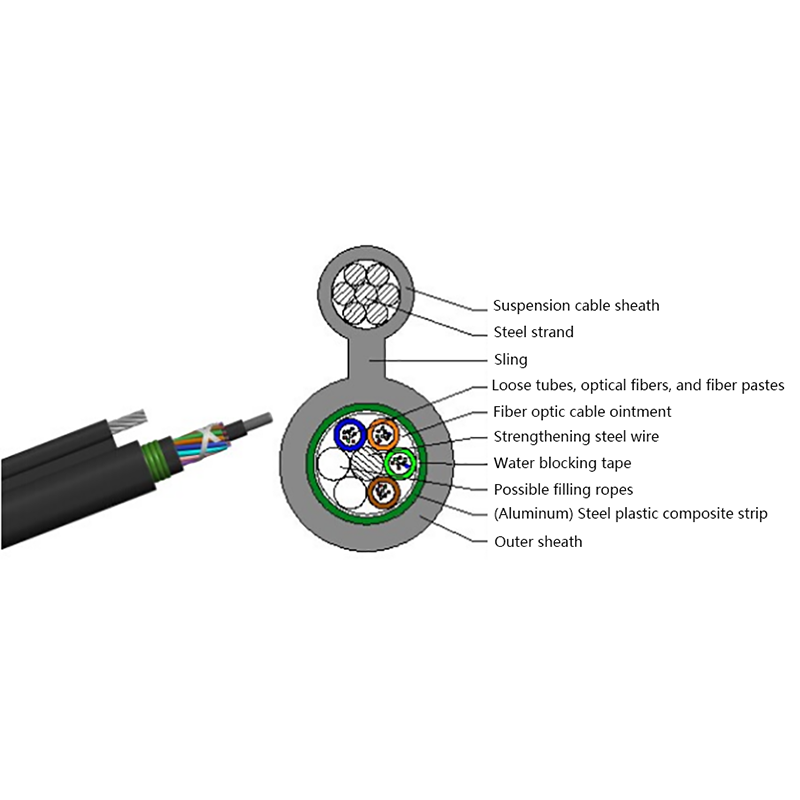
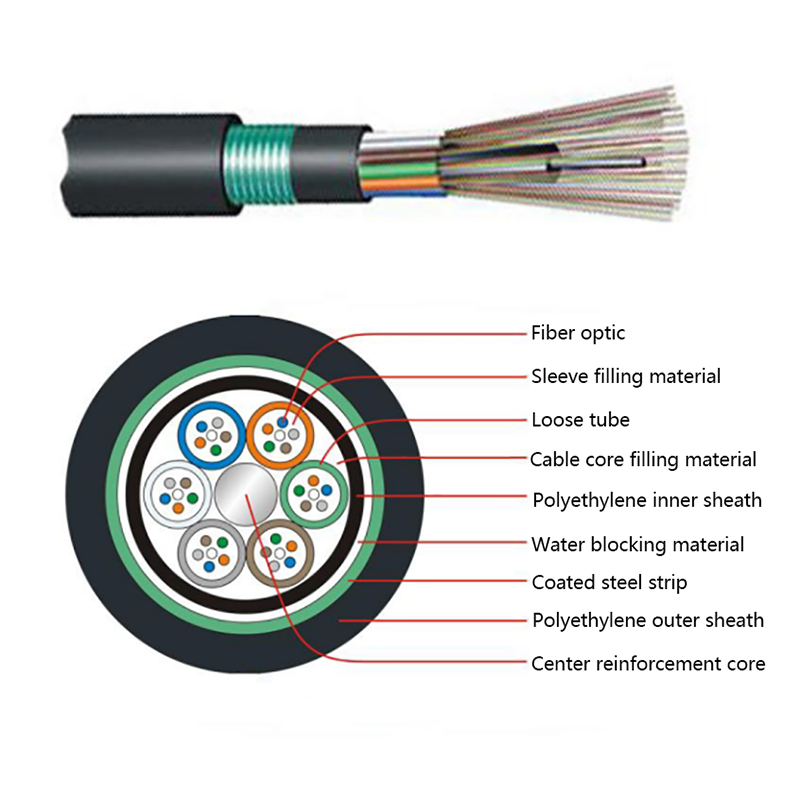
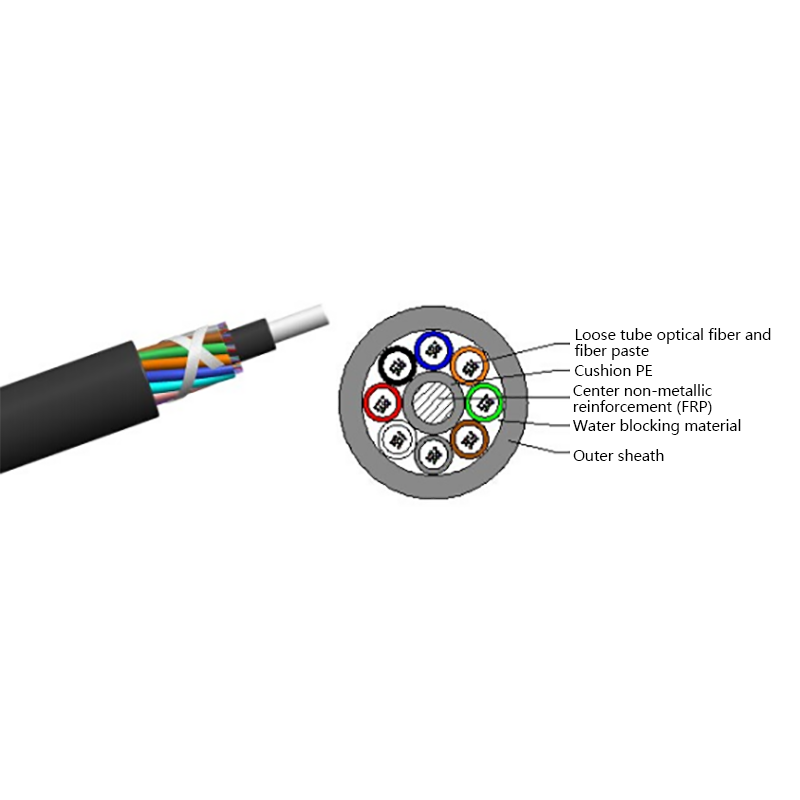
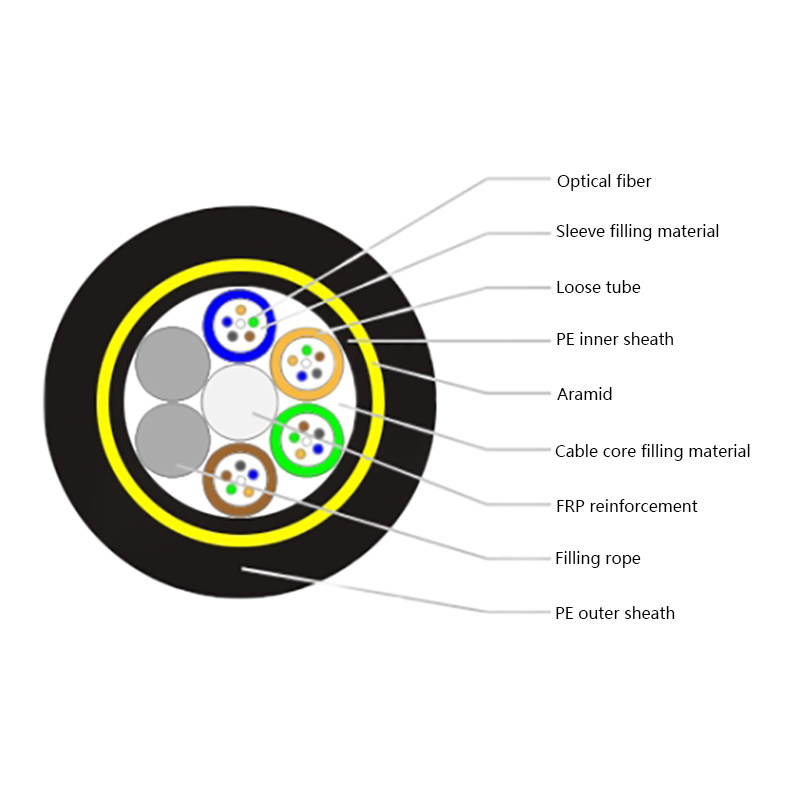
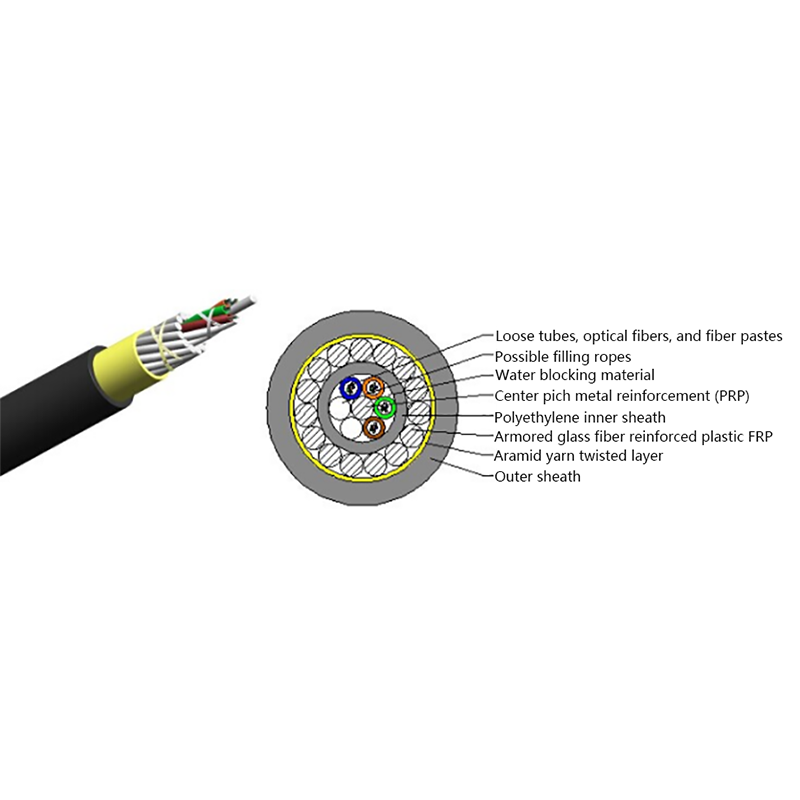
The performance of ADSS cables is closely tied to their internal structure and material selection. Each component is engineered to balance tensile strength, electrical insulation, and environmental resistance. Understanding this structure helps engineers choose the correct cable for specific span lengths and voltage environments.
Primary Structural Components
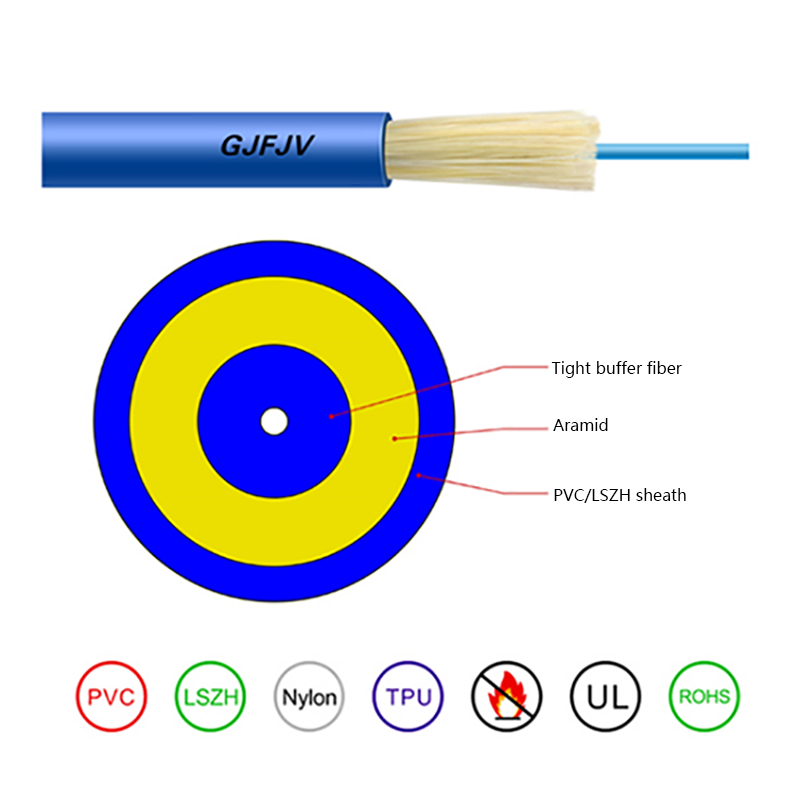
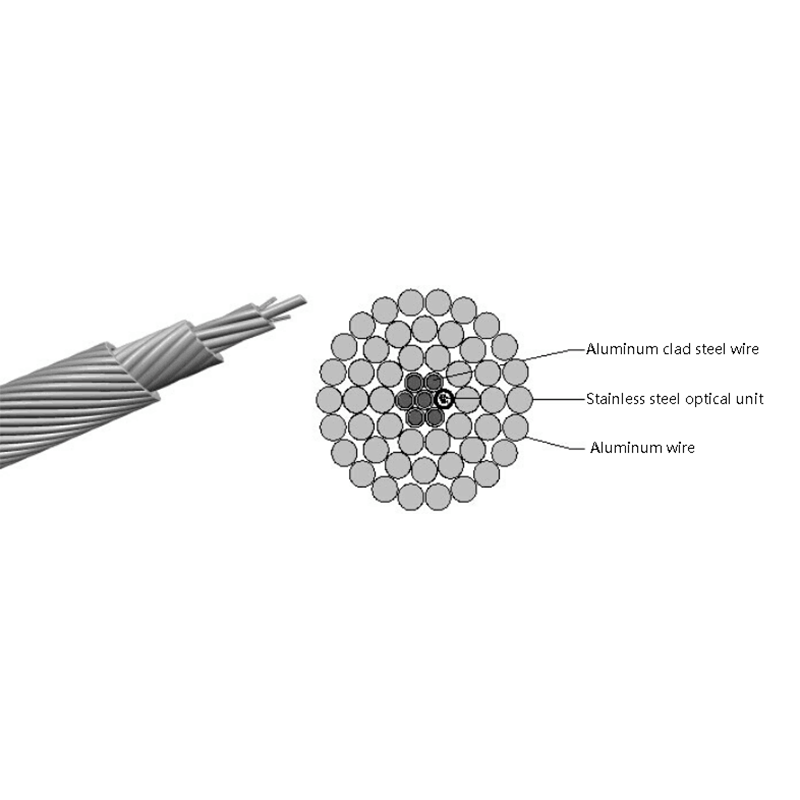
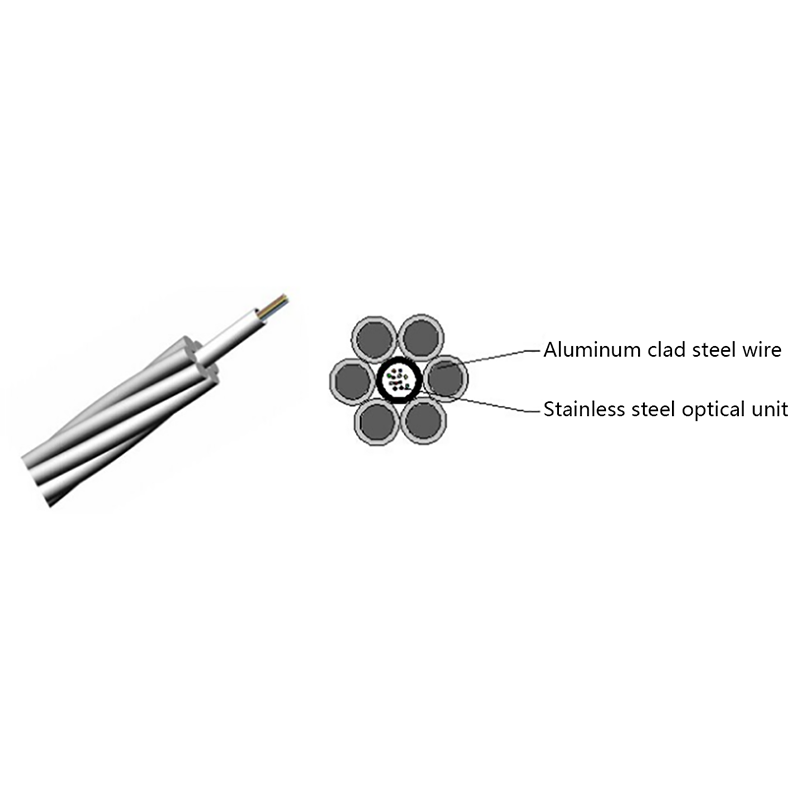
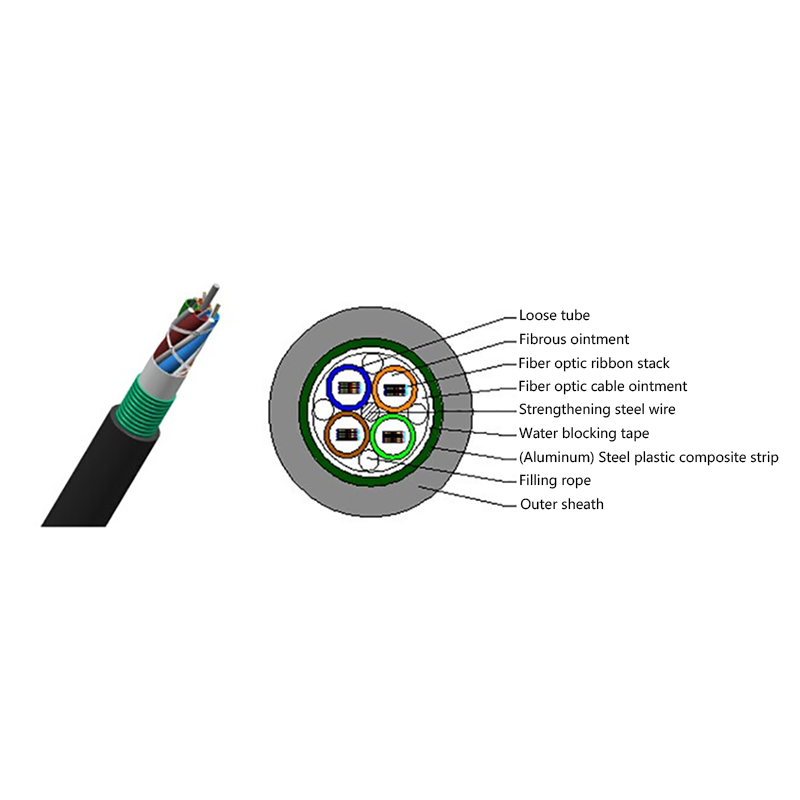
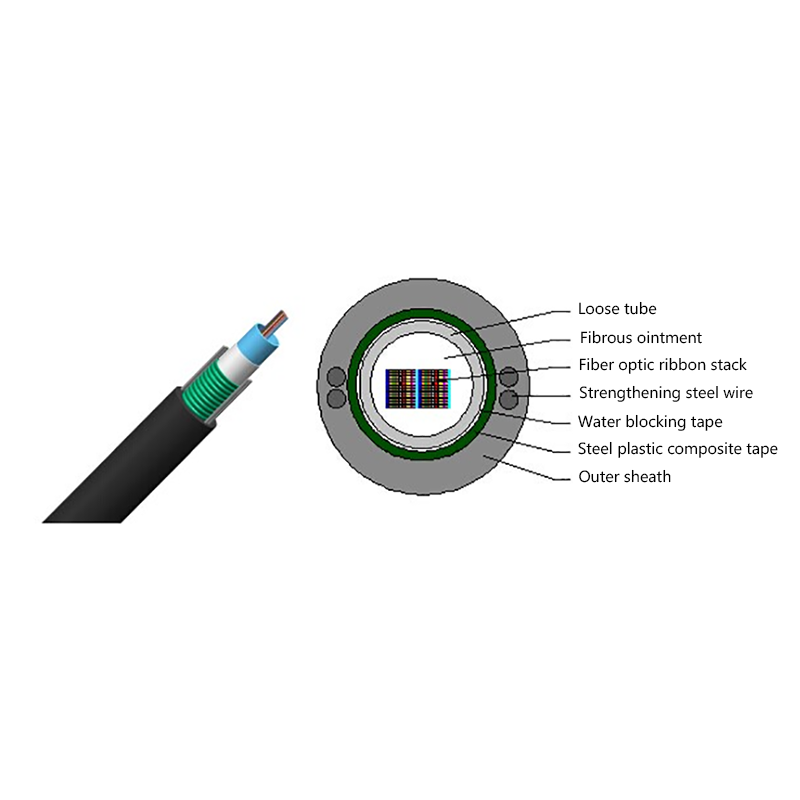
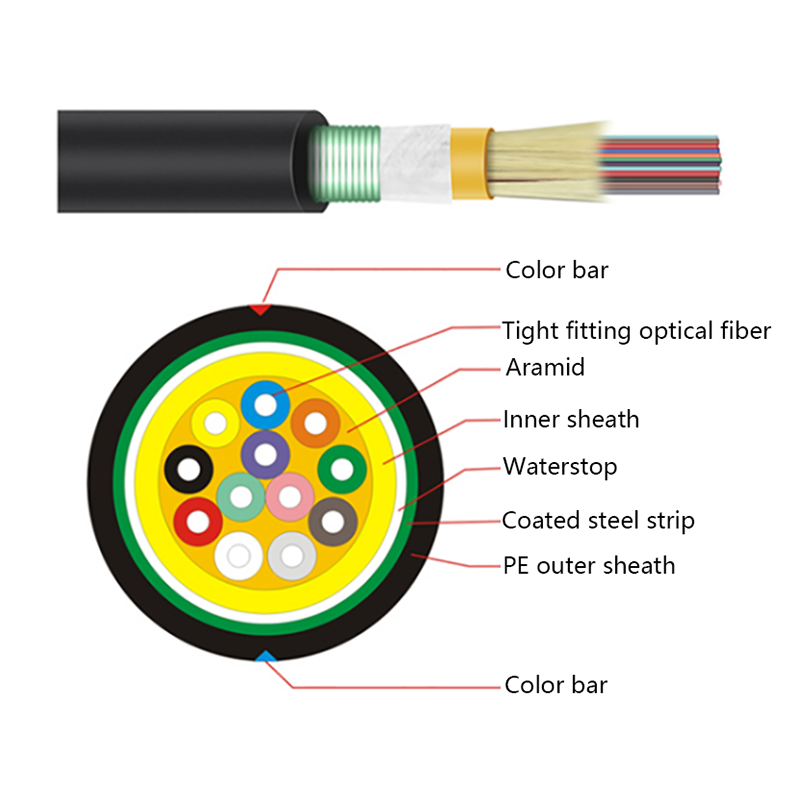
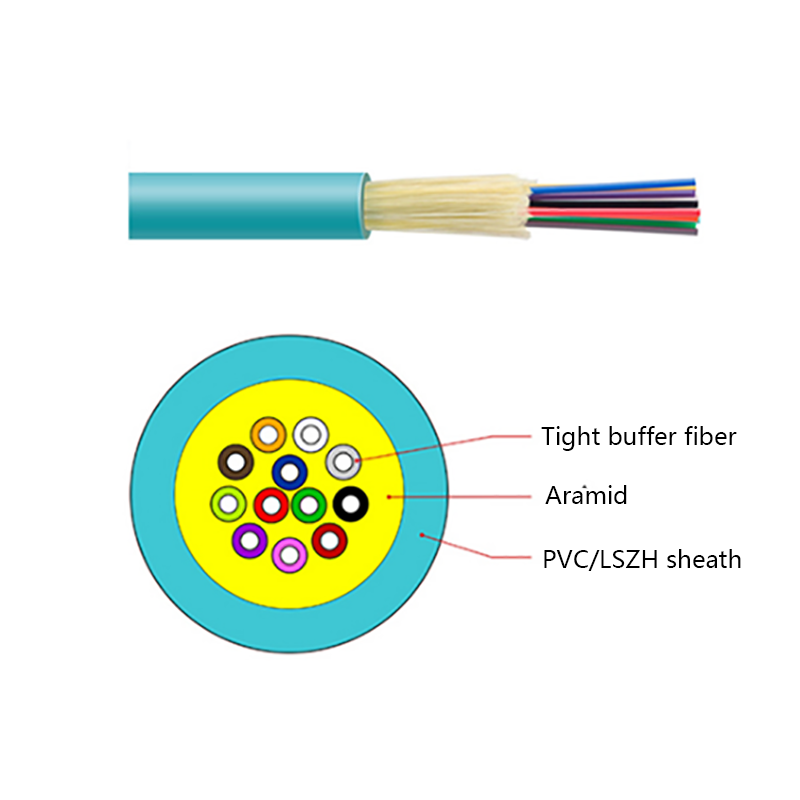
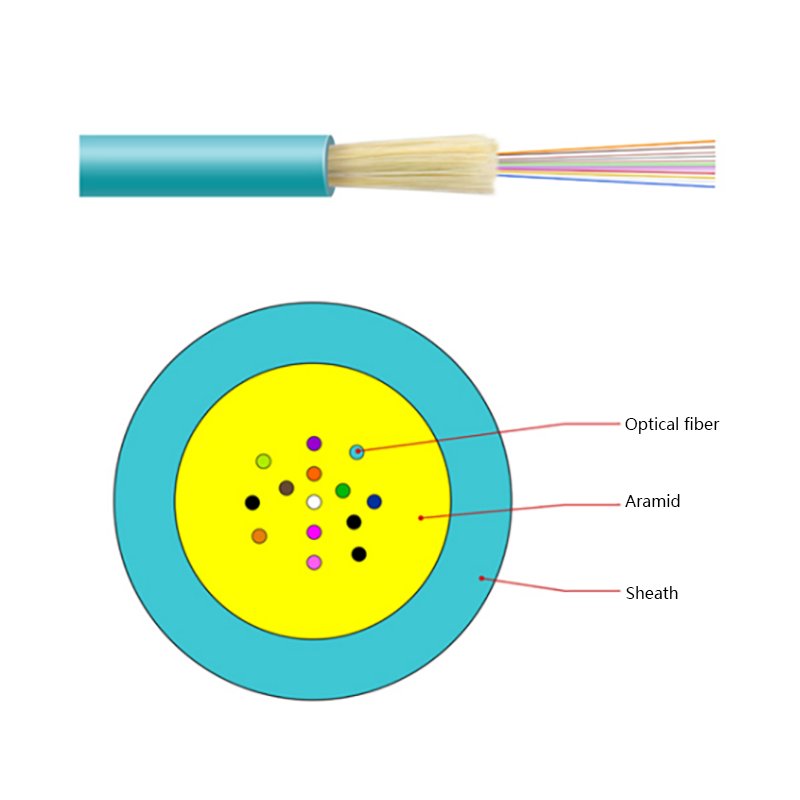
- Optical fiber core: Single-mode fibers optimized for long-distance, low-loss transmission, commonly compliant with ITU-T G.652D or G.657 standards.
- Loose tube layer: PBT or similar materials filled with water-blocking gel to protect fibers from moisture and mechanical stress.
- Strength members: Aramid yarns provide high tensile strength while remaining non-conductive.
- Outer sheath: UV-resistant polyethylene designed for long-term outdoor exposure.
Why ADSS Cables Are Ideal for Power Line Deployment
One of the most significant advantages of ADSS cables is their suitability for installation alongside high-voltage power lines. Because the cable contains no metallic elements, it avoids induced currents and electromagnetic interference. This makes ADSS cables especially valuable for utility companies seeking to deploy fiber optic communication systems on existing transmission infrastructure without compromising safety.
Key Operational Benefits
- Electrical insulation eliminates grounding requirements and reduces installation complexity.
- High tensile strength supports long spans between poles or towers.
- Resistance to electromagnetic interference ensures stable signal transmission.
Span Length and Mechanical Performance Considerations
Selecting the correct ADSS cable requires careful evaluation of span length, sag, wind pressure, and ice load. Manufacturers typically classify ADSS cables by short-span, medium-span, and long-span applications. Each classification uses different quantities of aramid yarn and sheath thickness to achieve the required mechanical strength.
| Span Type | Typical Span Length | Common Application |
| Short Span | Up to 100 m | Urban distribution networks |
| Medium Span | 100–300 m | Suburban and rural lines |
| Long Span | 300–1500 m | High-voltage transmission corridors |
Environmental Resistance and Service Life
ADSS cables are designed for harsh outdoor environments. UV radiation, temperature fluctuation, humidity, and chemical pollution can all degrade cable performance if materials are poorly selected. High-quality ADSS cables use anti-tracking outer sheaths that resist electrical discharge and surface erosion, especially in high-voltage environments.
Environmental Protection Features
- UV-stabilized jackets prevent cracking and fading under prolonged sunlight exposure.
- Water-blocking compounds reduce the risk of moisture penetration and fiber attenuation.
- Anti-tracking materials minimize surface discharge in polluted or coastal areas.
Installation Best Practices for ADSS Cables
Proper installation is critical to achieving long-term reliability. Unlike underground fiber optic cables, ADSS cables are continuously exposed to mechanical forces. Incorrect tension control or improper hardware selection can significantly reduce service life.
Practical Installation Guidelines
- Conduct accurate sag and tension calculations before deployment.
- Use dedicated ADSS suspension and tension clamps to avoid sheath damage.
- Maintain safe clearance distances from energized conductors.
Common Applications and Use Cases
ADSS cables are widely deployed across multiple industries. Their flexibility and electrical safety make them suitable for both communication operators and utility companies seeking reliable fiber optic solutions.
Typical applications include backbone fiber networks, FTTH aerial distribution, smart grid communication systems, and long-distance intercity links. In developing regions, ADSS cables reduce infrastructure costs by leveraging existing power line corridors without additional civil construction.
Choosing the Right ADSS Cable for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate ADSS cable involves balancing mechanical strength, fiber count, environmental resistance, and budget. Buyers should evaluate span length requirements, voltage levels, and local climate conditions before finalizing specifications. Working with experienced manufacturers and requesting detailed technical data can significantly reduce project risk and long-term maintenance costs.



 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体