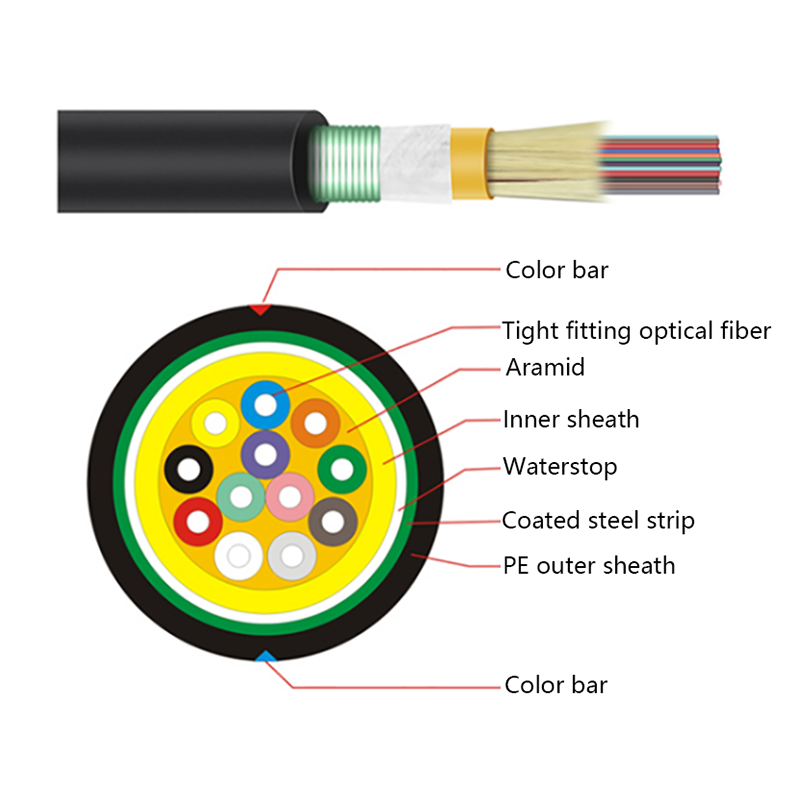
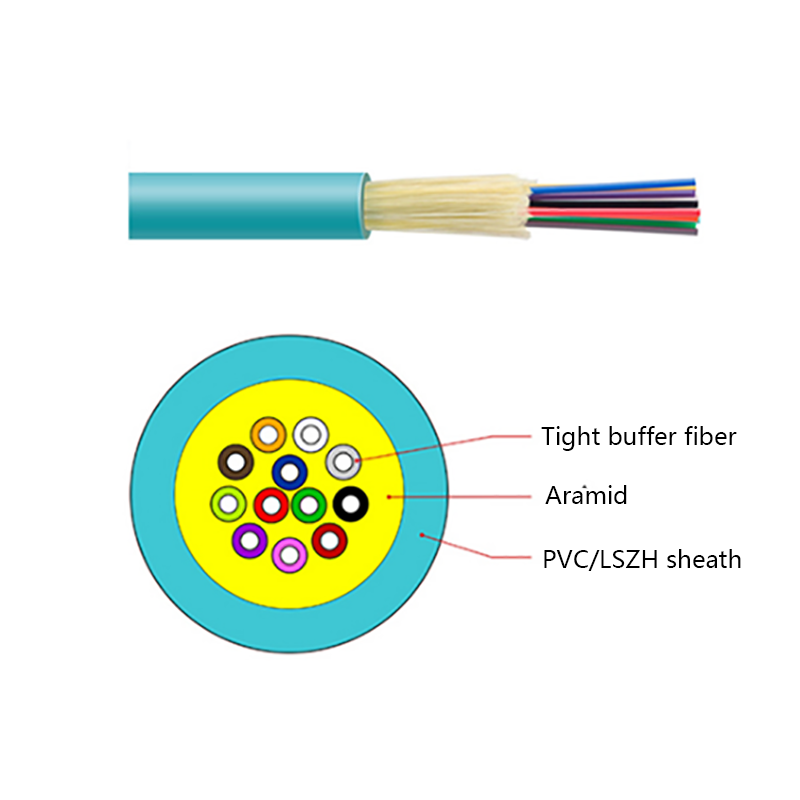
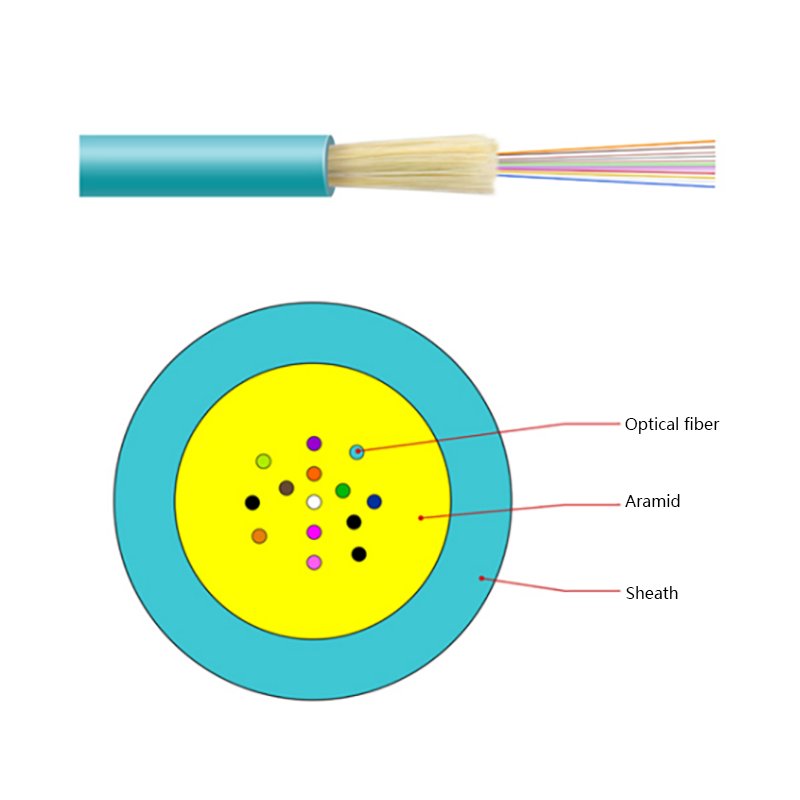
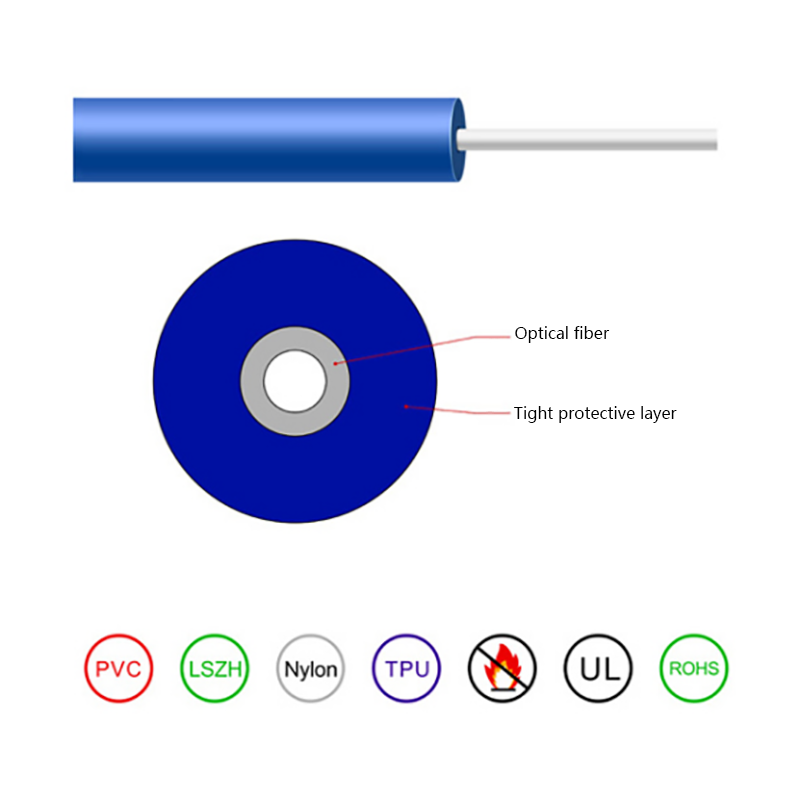
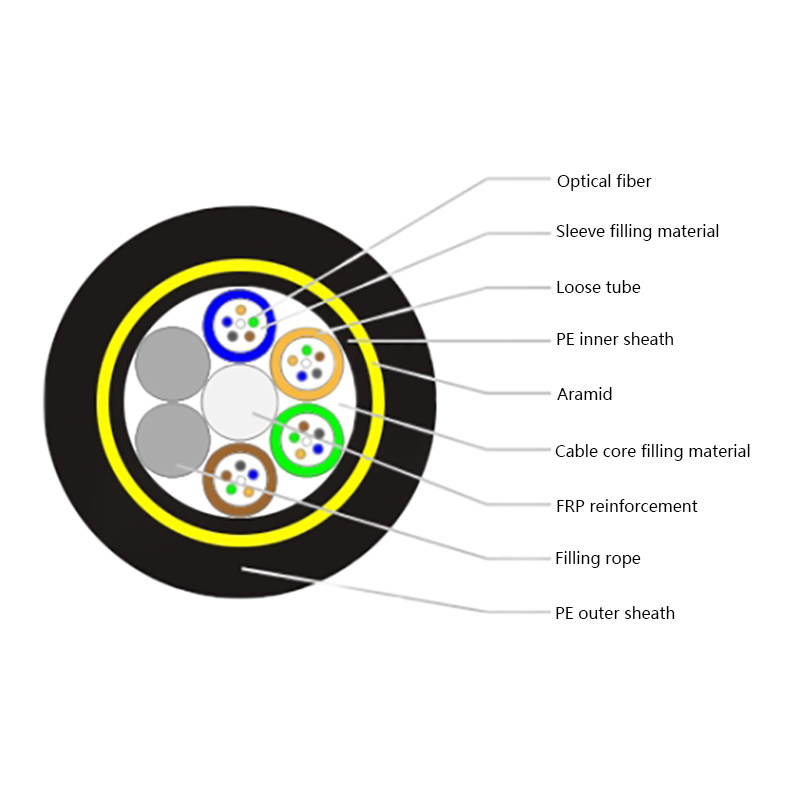
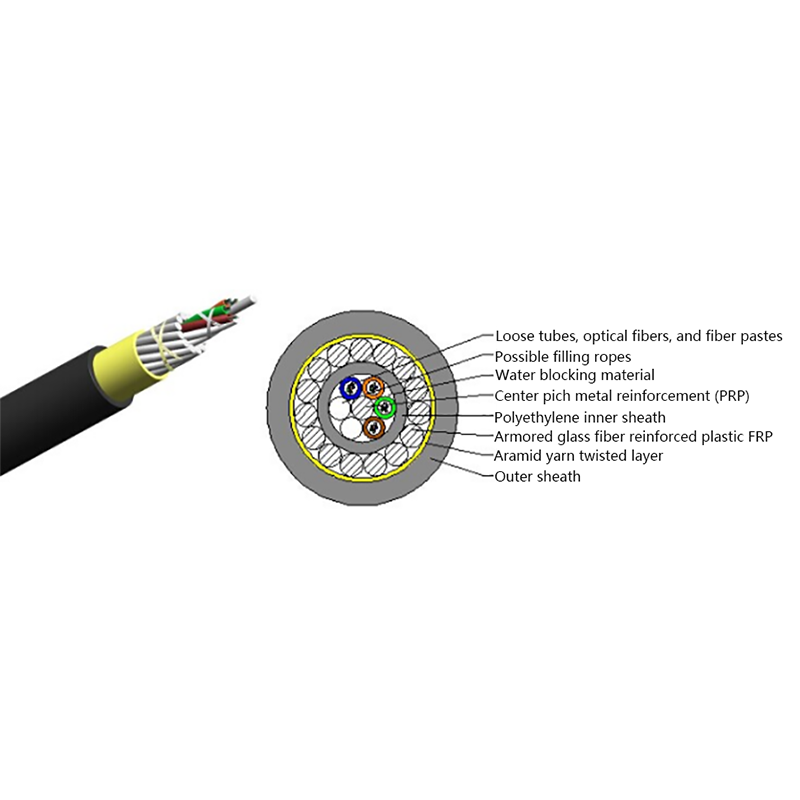
Hybrid Solutions Combined with Fiber Optic Cables: Practical Design, Installation, and Use Cases
Understanding What “Combined with Fiber Optic Cables” Means in Practice
When professionals refer to systems combined with fiber optic cables, they usually mean integrated cable solutions that merge optical fibers with other transmission or power elements in a single sheath. These combinations are designed to simplify infrastructure, reduce installation time, and improve reliability in modern networks. Instead of deploying separate cables for data, power, or signaling, hybrid fiber optic cables deliver multiple functions through one structured assembly.
This approach is widely used in telecommunications, industrial automation, security systems, and broadband access networks. By combining fiber optic cables with copper conductors or power lines, installers can meet both high-speed data transmission and electrical supply requirements without increasing cable density or complexity.
Common Types of Cables Combined with Fiber Optic Cables
Different combinations exist depending on the application and environment. Each type addresses specific technical and operational needs while maintaining the core advantage of fiber optic performance.
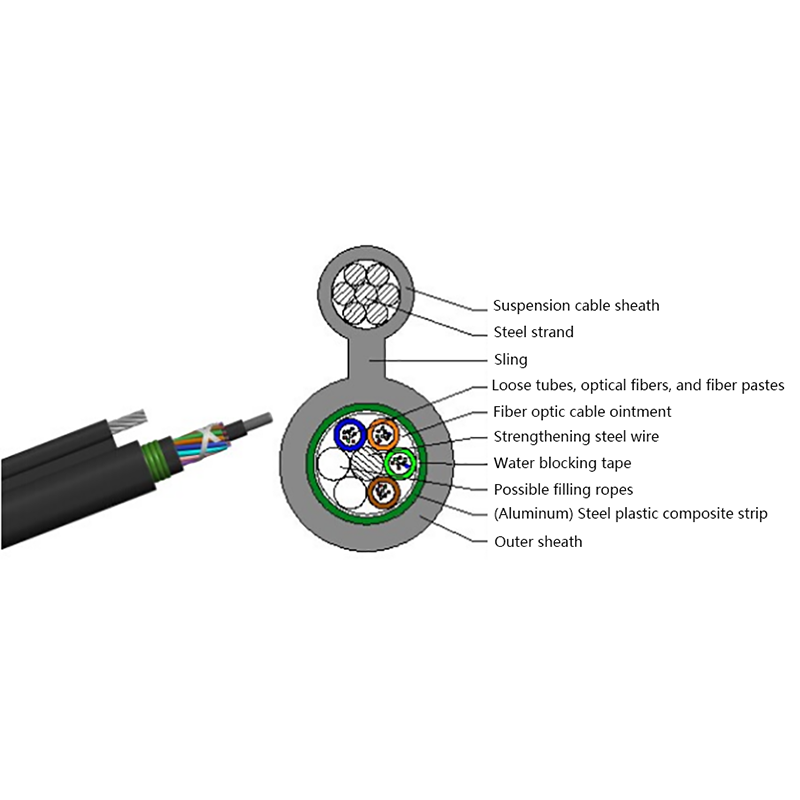
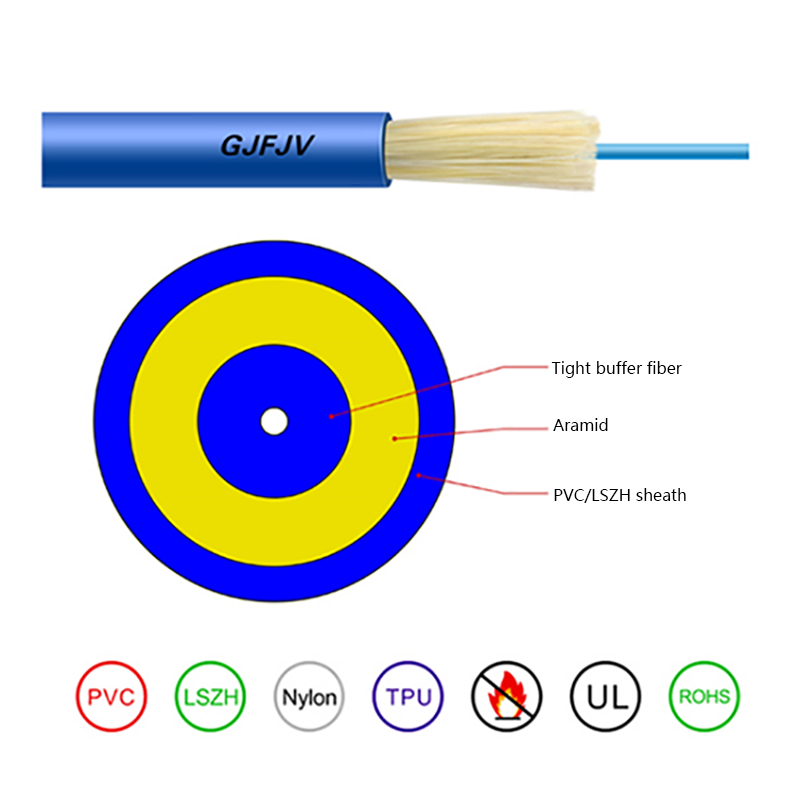
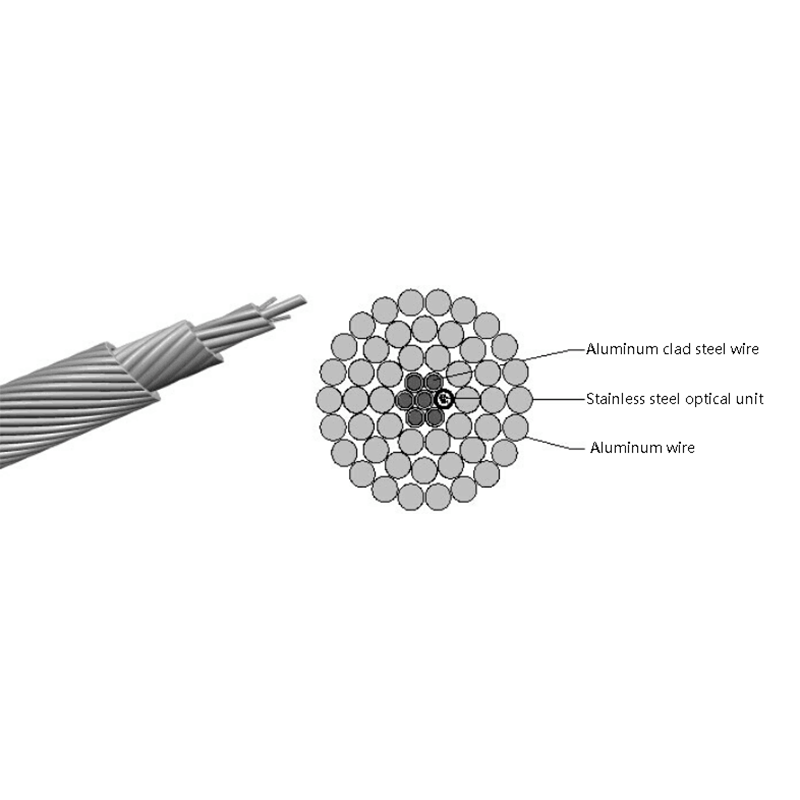
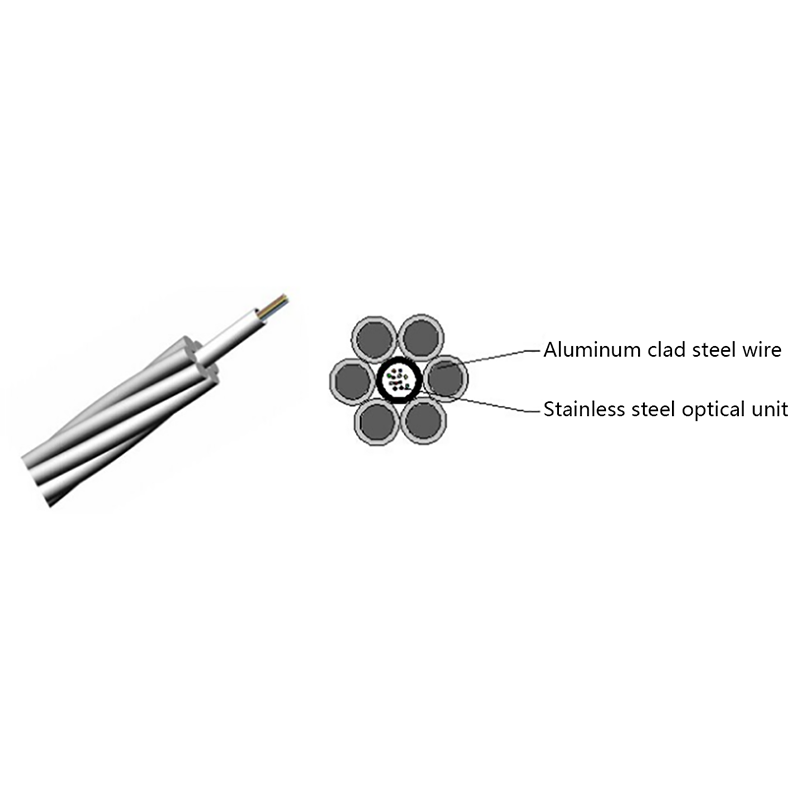
- Fiber and power hybrid cables: Integrate optical fibers with copper power conductors to support devices such as remote radio units, cameras, and access points.
- Fiber and coaxial combinations: Used in certain broadcast and legacy systems where optical data transmission and RF signals coexist.
- Fiber and control cables: Combine fibers with low-voltage control wires for industrial machinery and automation systems.
Each configuration is engineered to maintain optical signal integrity while ensuring electrical safety and compliance with relevant standards.
Why Combine Power and Data with Fiber Optic Cables
The primary reason for combining power and data in fiber optic cables is efficiency. Running separate cables for power and data increases material costs, installation labor, and maintenance complexity. Hybrid solutions reduce these burdens by delivering a single, unified infrastructure.
From a performance perspective, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, ensuring stable data transmission even when power conductors are present in the same cable. Proper insulation and shielding designs further enhance safety and reliability.
Key Advantages of Hybrid Fiber Optic Cable Systems
- Reduced installation time due to fewer cable runs
- Lower overall project cost for materials and labor
- Cleaner cable management in dense environments
- Improved scalability for future network expansion
Practical Applications Combined with Fiber Optic Cables
Hybrid fiber optic cables are used across many industries where high-speed data transmission and reliable power delivery are both required. Their design flexibility allows them to perform well in indoor, outdoor, and harsh industrial environments.
Telecommunications and FTTH Networks
In fiber-to-the-home deployments, combined fiber optic cables can supply power to remote network units while transmitting data back to the central office. This reduces the need for local power sources and simplifies network architecture, especially in rural or hard-to-access areas.
Security and Surveillance Systems
IP cameras, access control systems, and monitoring sensors often rely on hybrid fiber cables to deliver uninterrupted data streams and stable power. This is particularly valuable for long-distance outdoor installations where copper-only solutions would suffer from signal loss.
Industrial and Transportation Infrastructure
Factories, railways, and airports use combined fiber optic cables to connect control systems, sensors, and power modules. The durability of these cables ensures consistent performance under vibration, temperature changes, and mechanical stress.
Design Considerations When Using Hybrid Fiber Optic Cables
Selecting the right hybrid cable requires careful planning. Engineers must consider electrical load, fiber count, transmission distance, and environmental conditions. Ignoring these factors can lead to overheating, signal degradation, or premature cable failure.
Electrical and Optical Separation
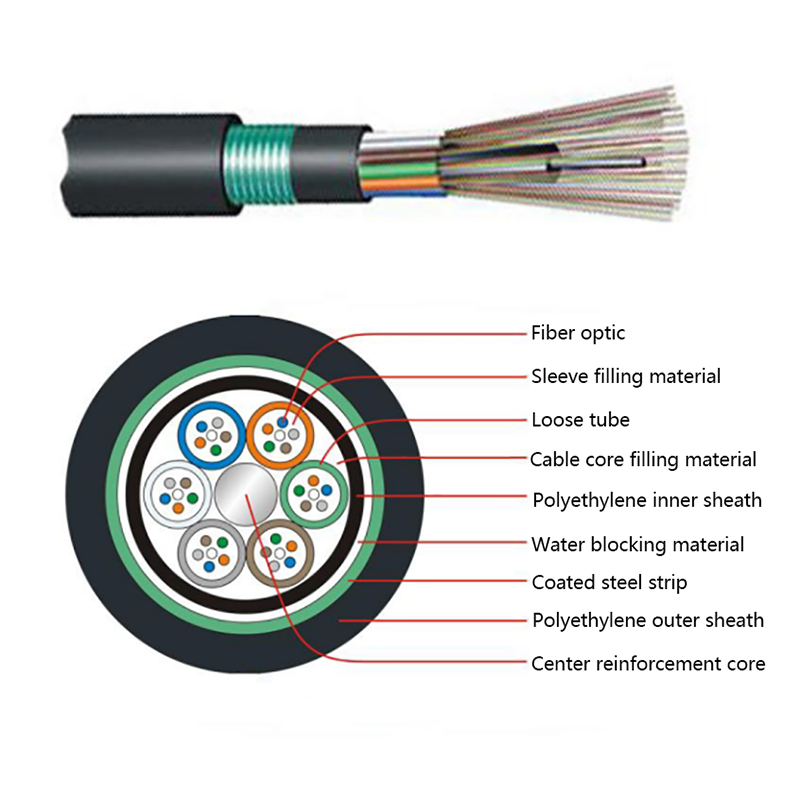
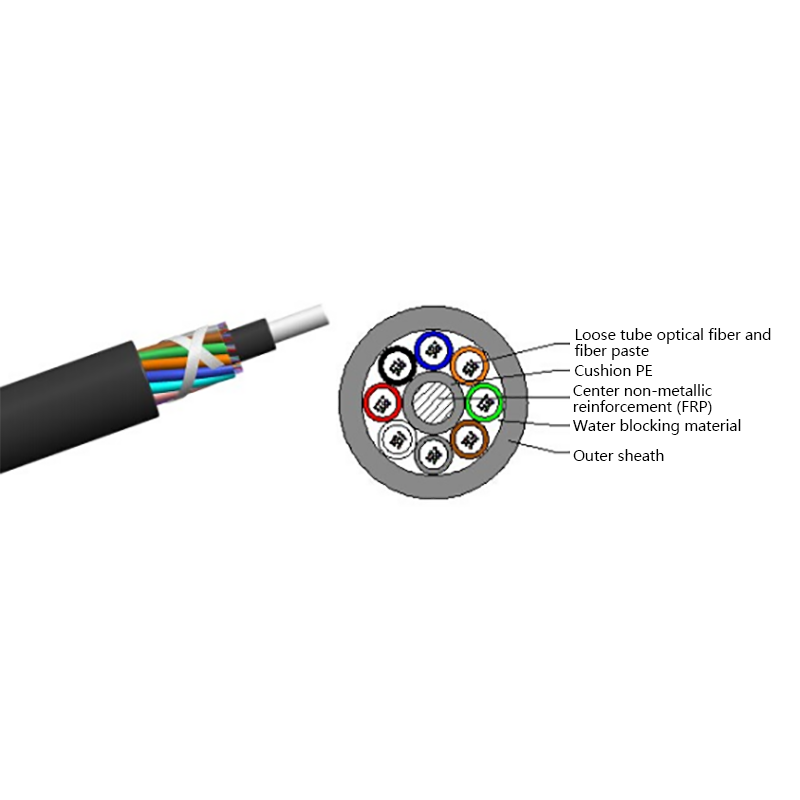
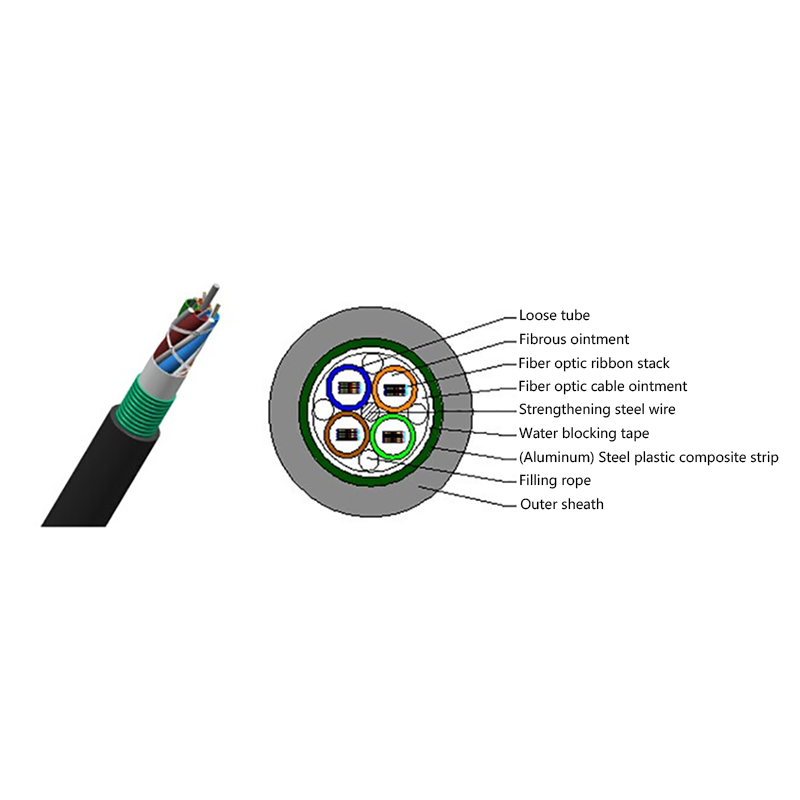
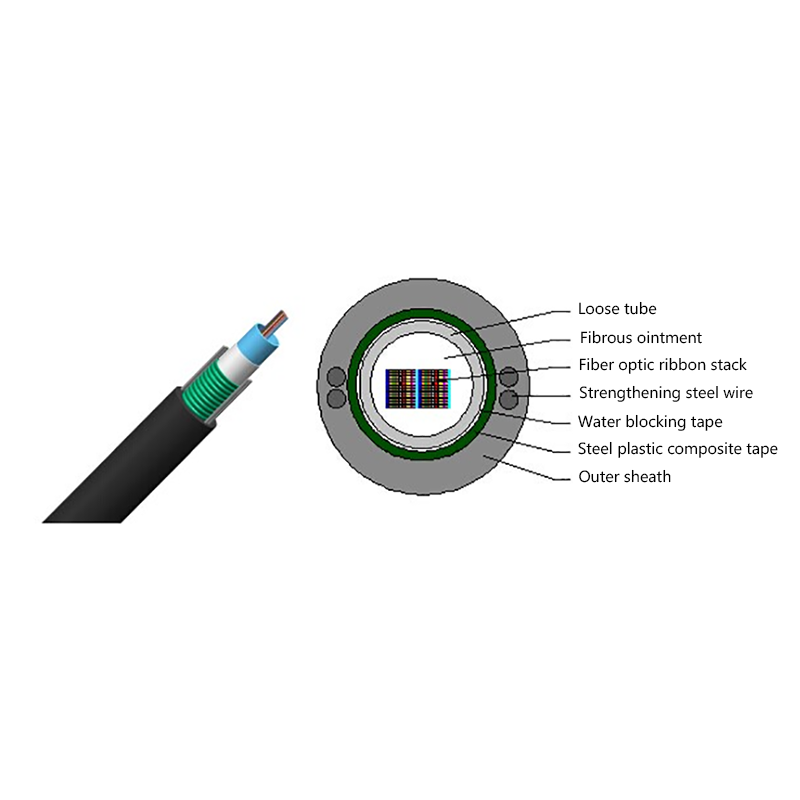
Proper internal separation between fiber optic elements and power conductors is critical. High-quality hybrid cables use layered insulation and buffering materials to protect optical fibers from heat and mechanical stress.
Environmental Protection
Outdoor installations require UV-resistant jackets, moisture barriers, and sometimes armored layers. For underground or industrial use, additional protection against chemicals and abrasion may be necessary.
Installation Best Practices for Combined Fiber Optic Cables
Even the best cable design can fail if installation practices are poor. Following industry-recommended procedures helps ensure long-term performance and safety.
- Observe minimum bend radius requirements for fiber optic cables
- Avoid excessive pulling tension during cable routing
- Clearly label power and fiber terminations at both ends
- Test optical loss and electrical continuity after installation
Comparison of Separate vs Combined Fiber Optic Cable Systems
| Aspect | Separate Cables | Combined Fiber Optic Cables |
| Installation Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Cable Management | More complex | Simplified |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
Maintenance and Long-Term Reliability
Maintaining systems combined with fiber optic cables involves routine inspection of jackets, connectors, and termination points. Hybrid cables reduce failure points by minimizing the number of separate connections, which directly improves long-term reliability.
Regular testing of optical attenuation and electrical load ensures that both data transmission and power delivery remain within safe and efficient operating ranges.
Future Trends in Fiber Optic Cable Integration
As networks evolve, the demand for integrated solutions combined with fiber optic cables continues to grow. Smart cities, 5G infrastructure, and industrial IoT deployments all benefit from compact, multifunctional cabling systems.
Future designs are expected to support higher power loads, increased fiber counts, and enhanced environmental protection, making hybrid fiber optic cables a central component of next-generation communication and control networks.



 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体