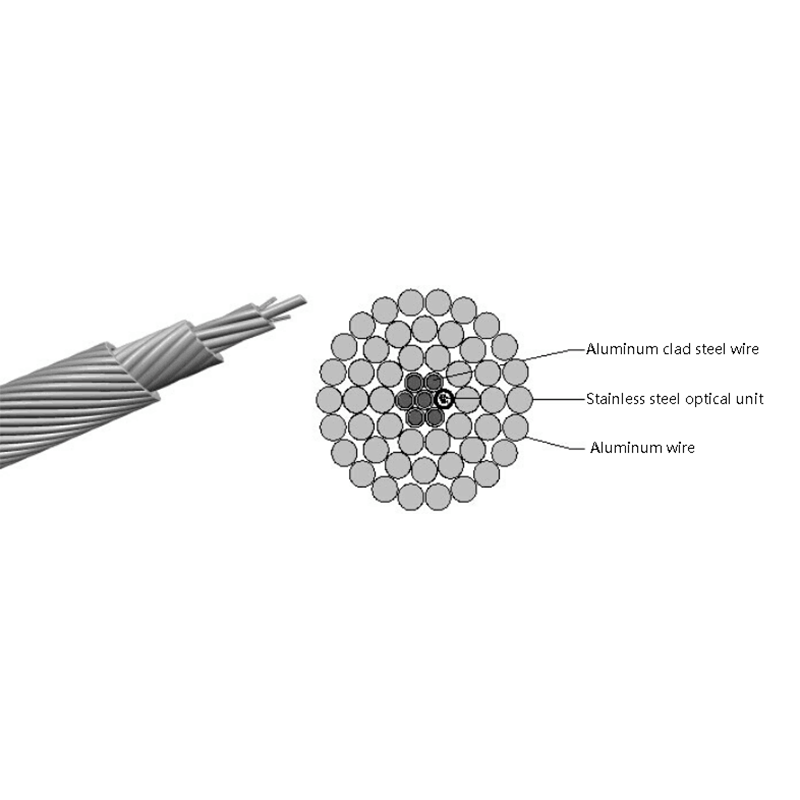
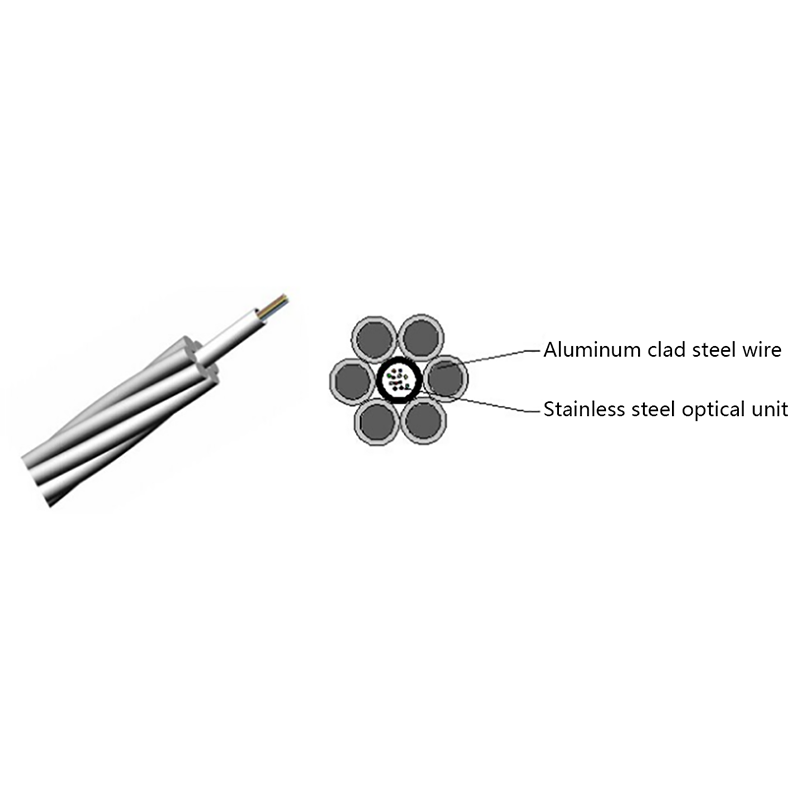
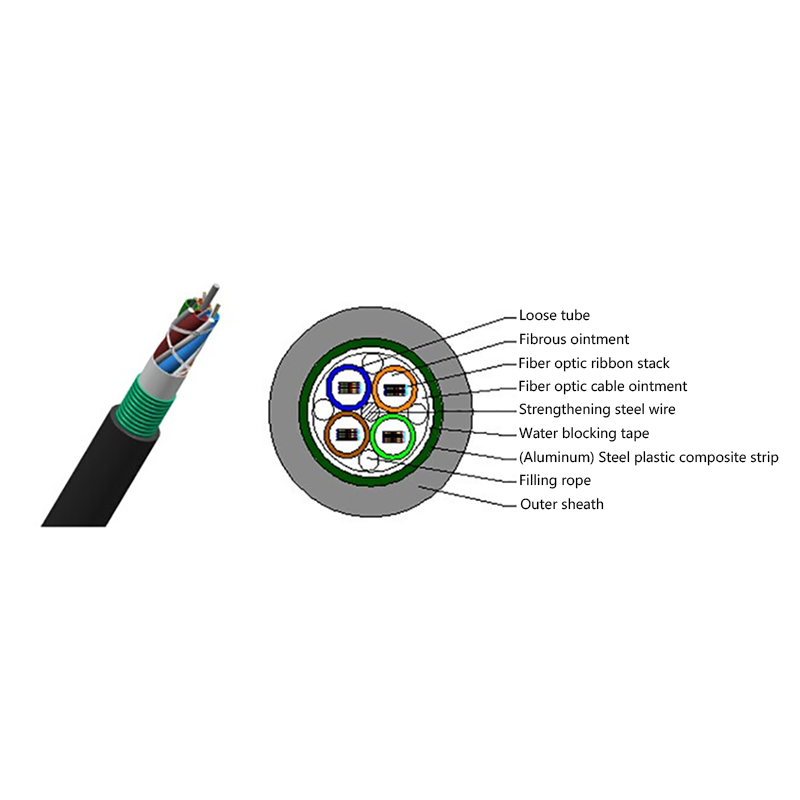
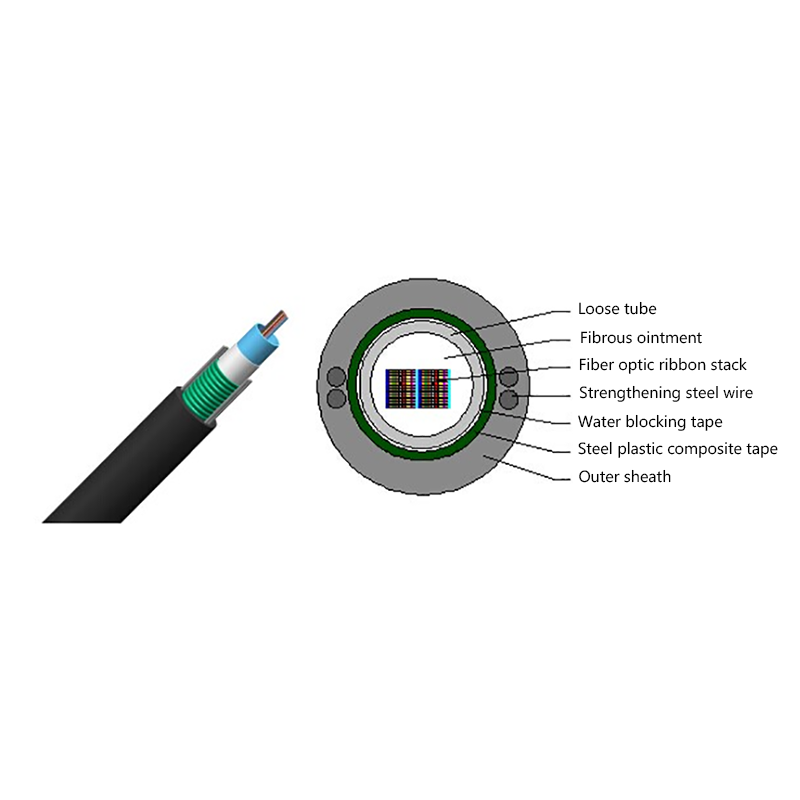
How do All Dielectric Self Supporting Cables Perform in High Wind or Ice Load Conditions?
In the field of modern telecommunications, the reliability of infrastructure often depends on how well it withstands environmental challenges. All Dielectric Self Supporting Cables (ADSS) are a critical part of fiber optic networks, especially where overhead installations are necessary. These cables are designed without metallic components, making them ideal for installation near high-voltage power lines and in areas where electromagnetic interference (EMI) could affect performance. However, one of the most important questions for engineers and network planners is: How do ADSS cables perform under high wind or ice load conditions?
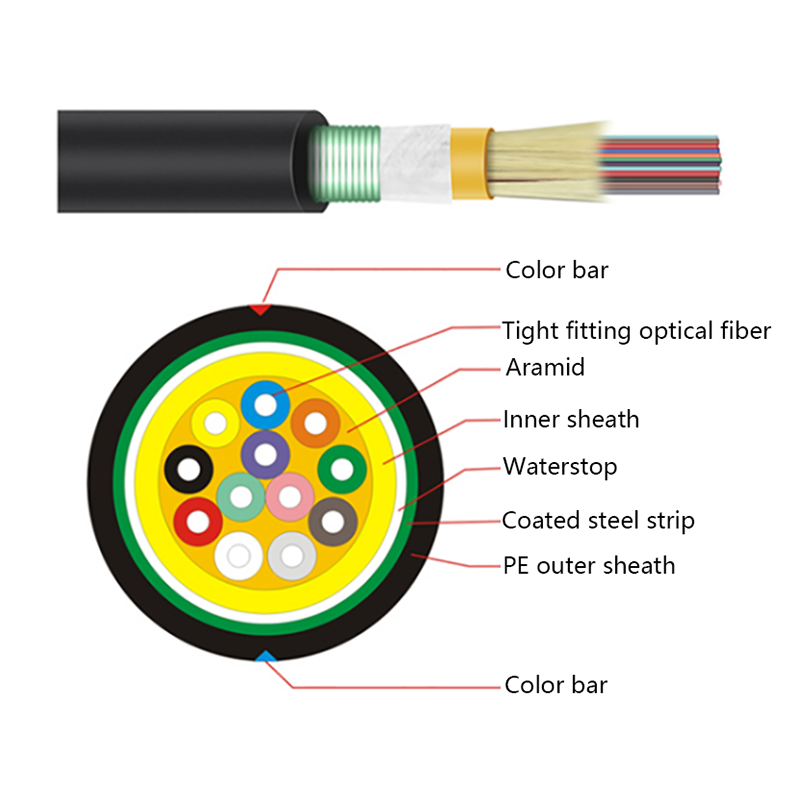
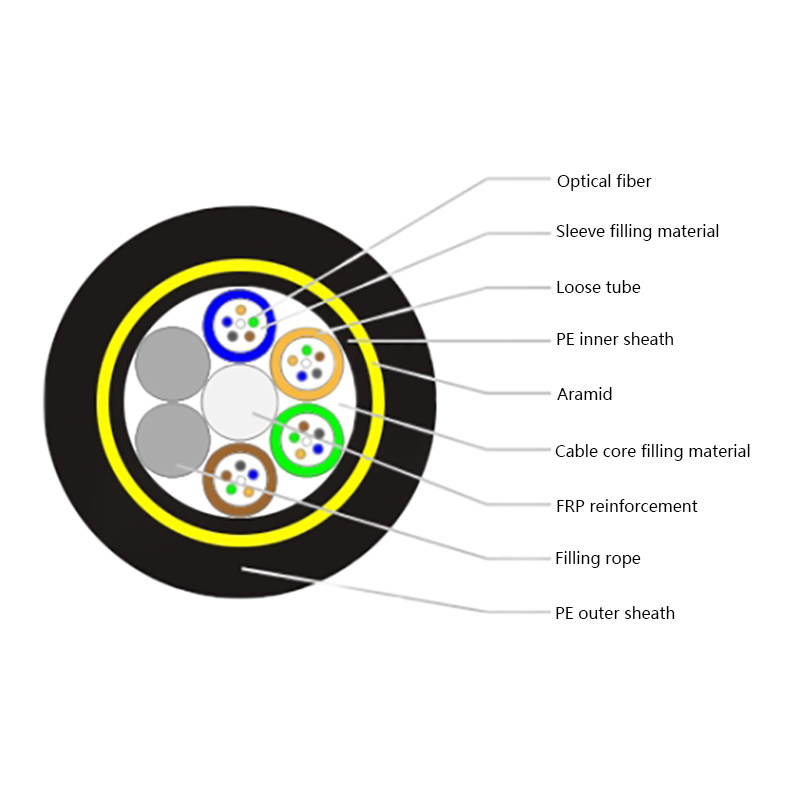
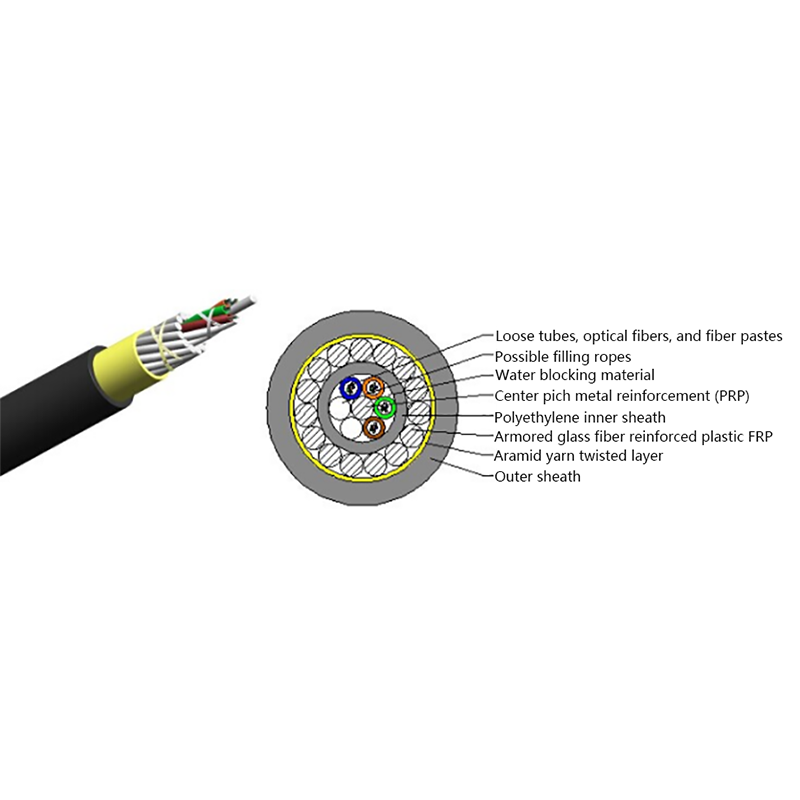
1. Understanding the Structure of All Dielectric Self Supporting Cables
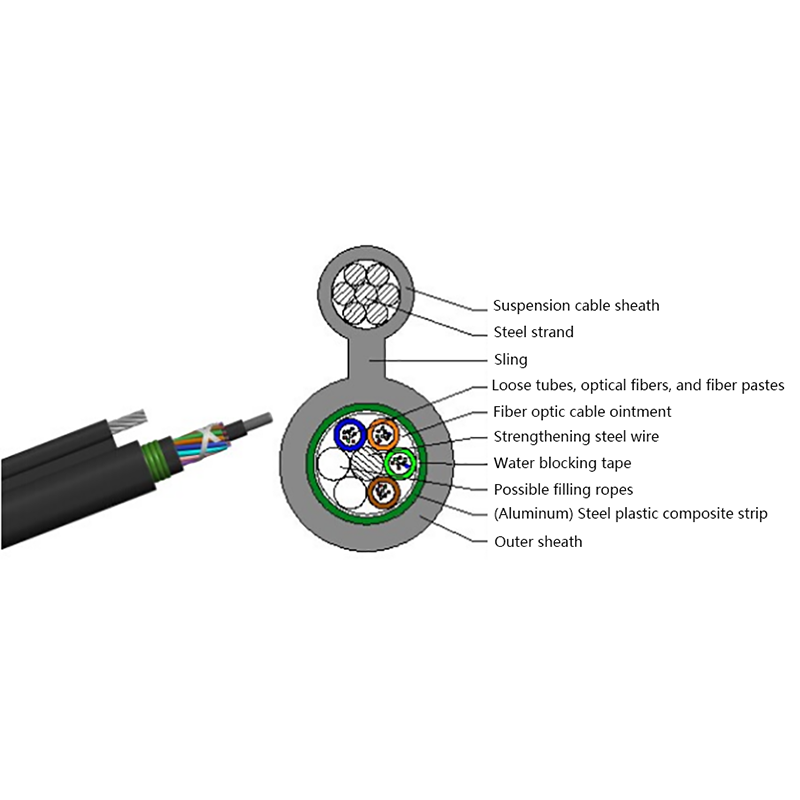
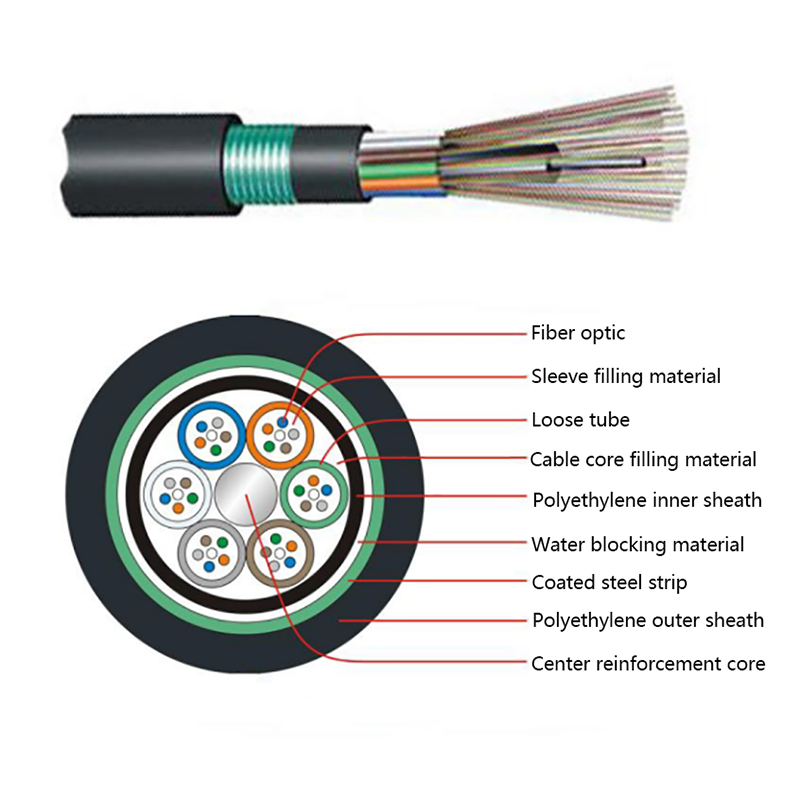
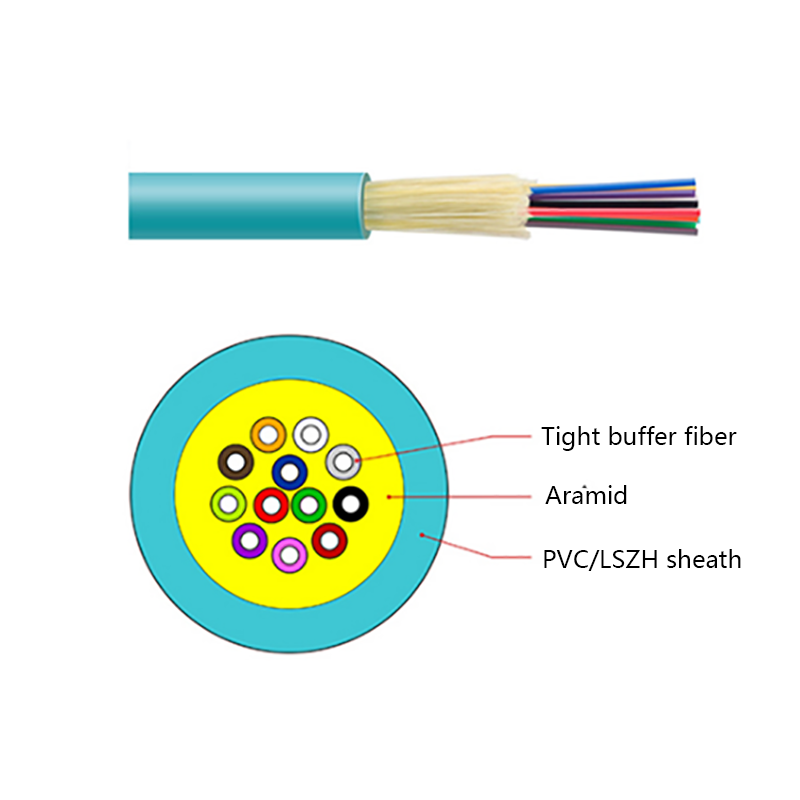
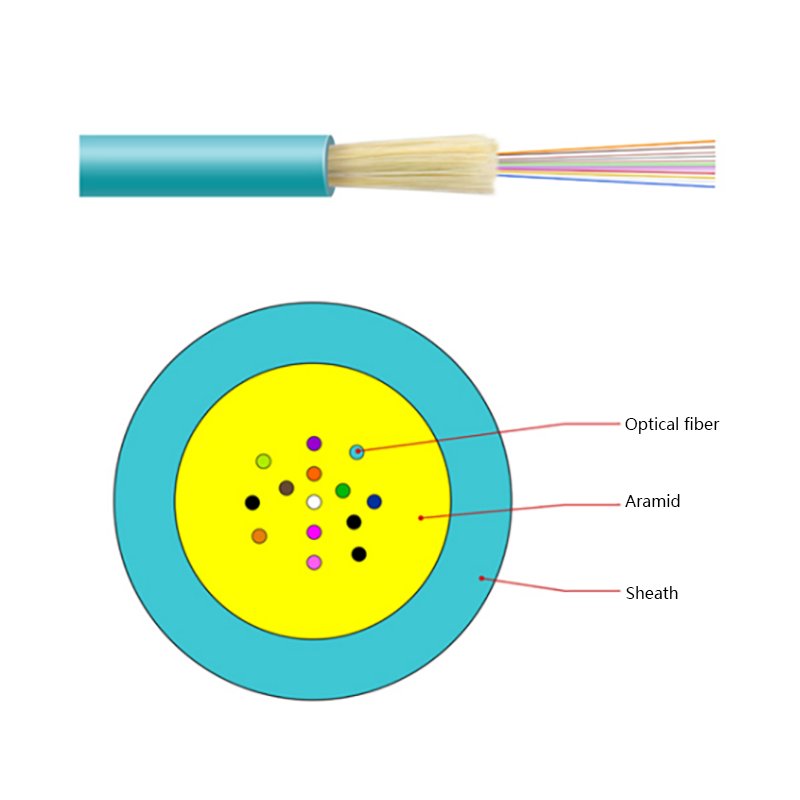
Before exploring their performance in extreme conditions, it is helpful to understand what makes ADSS cables unique. These cables are composed entirely of non-metallic materials, typically including:
- Central optical fibers, which carry data signals.
- A buffer tube that provides cushioning and protection for the fibers.
- Strength members, often made from aramid yarns (such as Kevlar), which give the cable its tensile strength and allow it to support its own weight across long spans.
- Outer jackets, usually made from UV-resistant polyethylene or similar materials, that protect against moisture, abrasion, and sunlight.
This “all-dielectric” design allows ADSS cables to be lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and free from electrical conductivity — all essential for aerial deployment near power lines.
2. Environmental Stress Factors: Wind and Ice Load
In outdoor aerial installations, two of the most severe mechanical stresses that cables face are wind pressure and ice accumulation.
- High Wind Conditions: When strong winds blow across a cable span, they create lateral forces that cause the cable to swing, vibrate, or oscillate. Over time, this motion can induce fatigue in the cable or its supporting hardware.
- Ice Load Conditions: In cold climates, freezing rain or high humidity can lead to the formation of ice on the cable’s surface. The weight of the ice significantly increases the load on the cable and its supports, potentially leading to sagging, mechanical stress, or even cable breakage if not properly accounted for.
The combined effect of wind and ice can amplify stress levels, as wind applies dynamic forces while ice increases static load. Therefore, the ability of ADSS cables to withstand these combined conditions is essential for their successful long-term operation.
3. Design Factors Influencing ADSS Cable Performance
a. Tensile Strength and Span Design
One of the key advantages of ADSS cables is their high tensile strength-to-weight ratio, achieved through the use of aramid yarns. These synthetic fibers distribute mechanical stress evenly along the cable and allow it to remain stable even under heavy ice loads.
Engineers typically calculate the maximum allowable span length based on the expected wind and ice conditions of a region. Shorter spans are often recommended in regions with heavy icing to reduce tension and the risk of mechanical failure.
b. Cable Diameter and Surface Finish
The outer diameter and smoothness of the cable surface directly affect how much ice accumulates and how wind acts upon it. A smaller-diameter cable presents less surface area for wind drag and ice buildup. Some manufacturers also apply low-friction or hydrophobic coatings that reduce ice adhesion, helping to minimize extra weight during winter conditions.
c. Material Resilience and Jacket Composition
The outer jacket of ADSS cables is designed to resist cracking and abrasion under fluctuating temperatures. In high wind areas, the jacket must also prevent wear caused by vibration or contact with support structures. UV stabilization is equally important since long-term exposure to sunlight can weaken the material and increase the risk of damage during high-stress conditions.
4. Vibration and Aeolian Effects Under Wind Load
One of the subtle but significant challenges faced by ADSS cables in high wind environments is aeolian vibration—a phenomenon caused by steady, low-speed winds (typically 3–25 mph). These winds can generate small, repetitive oscillations in the cable, leading to long-term fatigue damage in both the cable and its fittings.
To mitigate this effect, vibration dampers or spiral vibration control devices are commonly installed near attachment points. Proper tensioning during installation also plays a major role in reducing vibration amplitude and preventing premature wear. In particularly windy regions, double-layer protection or specialized clamp designs can further enhance stability.
5. Performance Under Ice Load Conditions
When ice begins to accumulate on an ADSS cable, several changes occur:
- The weight of the cable increases substantially.
- The tensile load on anchor points rises.
- The sag in the cable increases, which can alter clearances and introduce additional bending stress.
Modern ADSS cables are engineered to handle these situations through optimized mechanical strength and flexibility. Aramid yarn reinforcement ensures that even with additional ice weight, the optical fibers remain well-protected and continue to transmit signals without attenuation.
In extremely cold environments, cold-resistant jacket materials—often made from low-temperature polyethylene—are used to prevent brittleness and cracking. The use of proper cable geometry and support hardware designed for ice-prone regions helps maintain stability even under severe icing conditions.
6. Installation Practices for Adverse Weather Performance
Even a well-designed ADSS cable can perform poorly if not properly installed. Installation practices have a direct impact on how the cable reacts to environmental loads. Some key considerations include:
- Correct Tensioning: Ensuring the cable is neither too tight nor too slack helps balance performance during wind and ice events.
- Appropriate Span Lengths: Shorter spans and intermediate supports are advisable in high-risk areas.
- Hardware Selection: Using weather-rated clamps, supports, and vibration dampers helps extend service life.
- Clearance Planning: Ensuring adequate distance from power lines and other structures prevents contact or abrasion during cable movement.
Routine inspection after severe weather is also essential to detect potential damage before it leads to service interruptions.
7. Testing and Standards for Environmental Resistance
ADSS cables are tested under standardized conditions to simulate real-world environmental loads. Industry standards such as IEC 60794 and IEEE 1222 specify mechanical, environmental, and electrical requirements for these cables.
Tests may include:
- Tensile load testing under simulated ice weight
- Wind tunnel testing for aerodynamic behavior
- Temperature cycling to assess jacket performance
- UV and moisture resistance evaluation
Compliance with these standards ensures that ADSS cables are capable of withstanding demanding outdoor environments for decades.
8. Real-World Applications and Proven Reliability
The use of All Dielectric Self Supporting Cables in regions with extreme climates has proven their resilience. In northern countries with heavy snowfall, ADSS cables maintain connectivity despite ice buildup due to their lightweight yet strong construction. In coastal and mountainous regions, their non-metallic composition prevents corrosion and mitigates damage from salt or wind-driven debris.
Utilities and telecom operators often choose ADSS cables for power line communication systems, where both high wind and ice are frequent. Their ability to maintain consistent optical performance, even under mechanical strain, makes them a dependable solution for aerial installations.
9. Preventive Maintenance and Long-Term Performance
While ADSS cables are designed for minimal maintenance, preventive measures can enhance their longevity:
- Regular visual inspections after storms
- Monitoring sag and tension values
- Checking for signs of jacket wear or aramid yarn exposure
- Replacing worn vibration dampers or suspension hardware
With proper care, ADSS cables can operate reliably for 25 to 30 years even in areas prone to wind and ice.
Conclusion
All Dielectric Self Supporting Cable are engineered to endure some of the most challenging environmental conditions encountered in fiber optic network installations. Their combination of lightweight construction, high tensile strength, and non-conductive materials allows them to perform effectively under both high wind and ice load conditions.
While environmental stresses can never be entirely eliminated, careful selection of cable design, precise installation techniques, and adherence to maintenance best practices can ensure long-term performance and reliability. Whether deployed across open fields, mountain ridges, or coastal power corridors, ADSS cables continue to prove that robust engineering and thoughtful design make it possible to achieve both strength and stability in demanding environments.



 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体