Practical Guide to Air Blown Micro Cables: Design, Installation, and Use Cases
Air Blown Micro Cables are a core component of modern fiber deployment strategies, especially where flexibility, scalability, and reduced civil work are priorities. Unlike traditional pulled fiber cables, these micro cables are installed using compressed air, allowing long-distance installation with minimal mechanical stress. This article focuses on how they work, how they are deployed, and what practical considerations matter most in real projects.
What Air Blown Micro Cables Are and How They Work
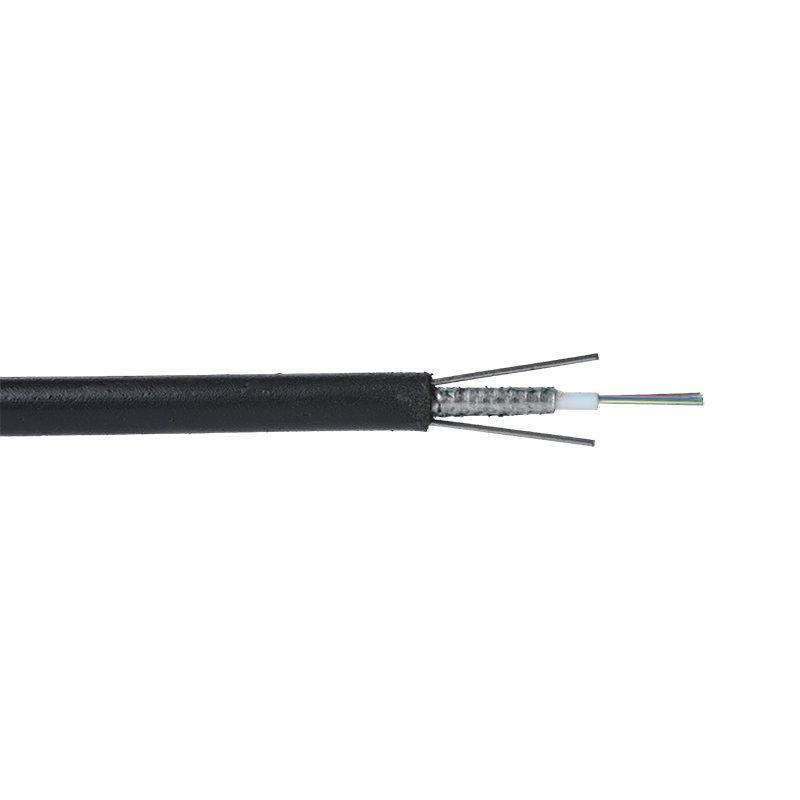
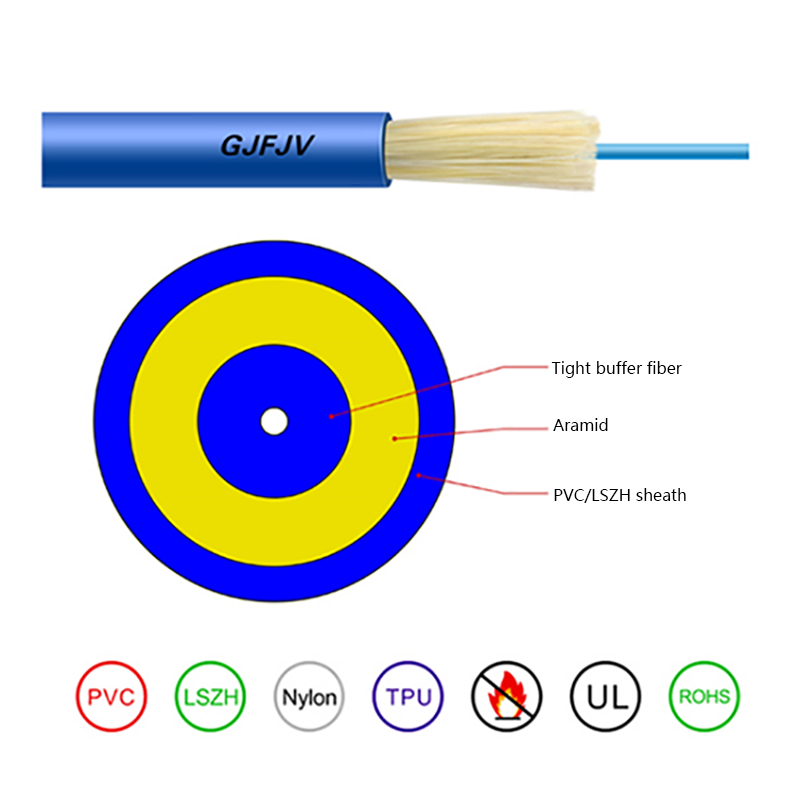
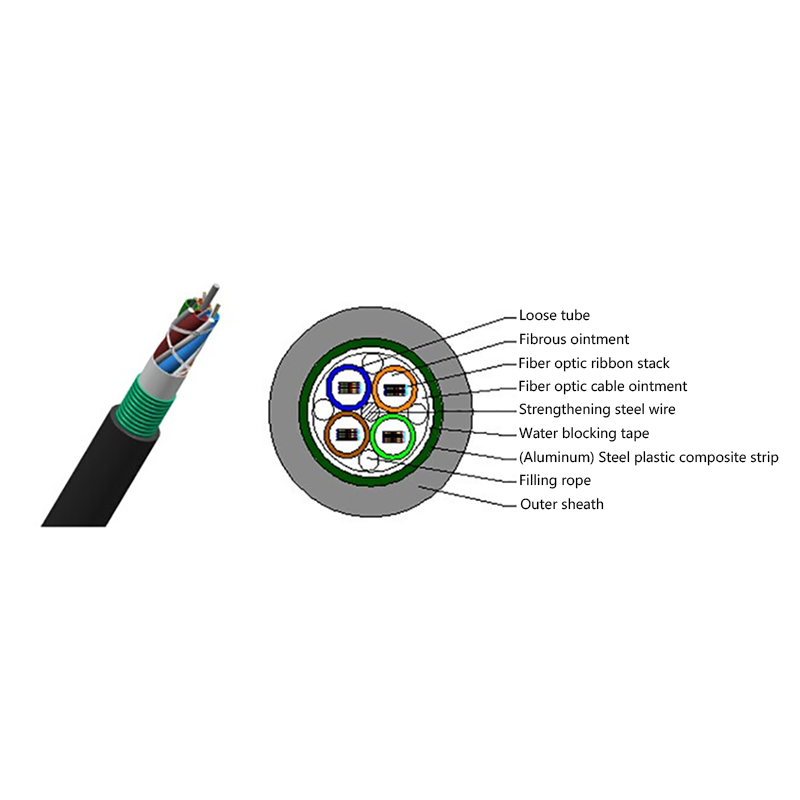
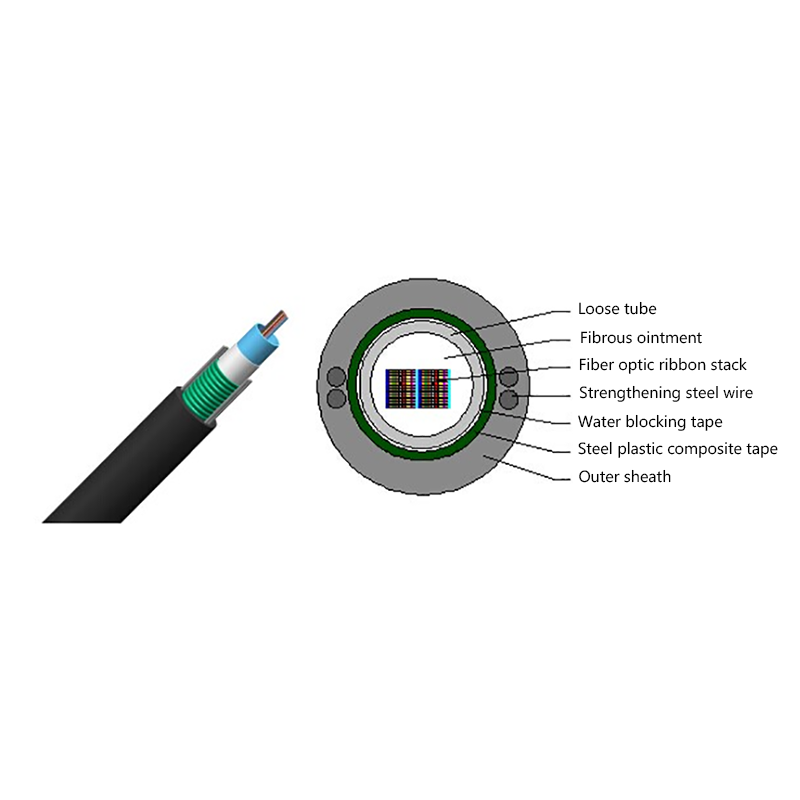
Air Blown Micro Cables are lightweight fiber optic cables designed specifically to be installed inside microducts using a jetting or blowing technique. Compressed air propels the cable through the duct, significantly reducing friction compared to pulling methods. The cable effectively floats on an air cushion while being pushed forward by a controlled mechanical force.
This installation method allows cables to be installed over longer distances in a single run, often exceeding 1–2 kilometers depending on duct quality, cable design, and blowing equipment. Because tensile stress is minimized, fiber attenuation remains stable even after installation.
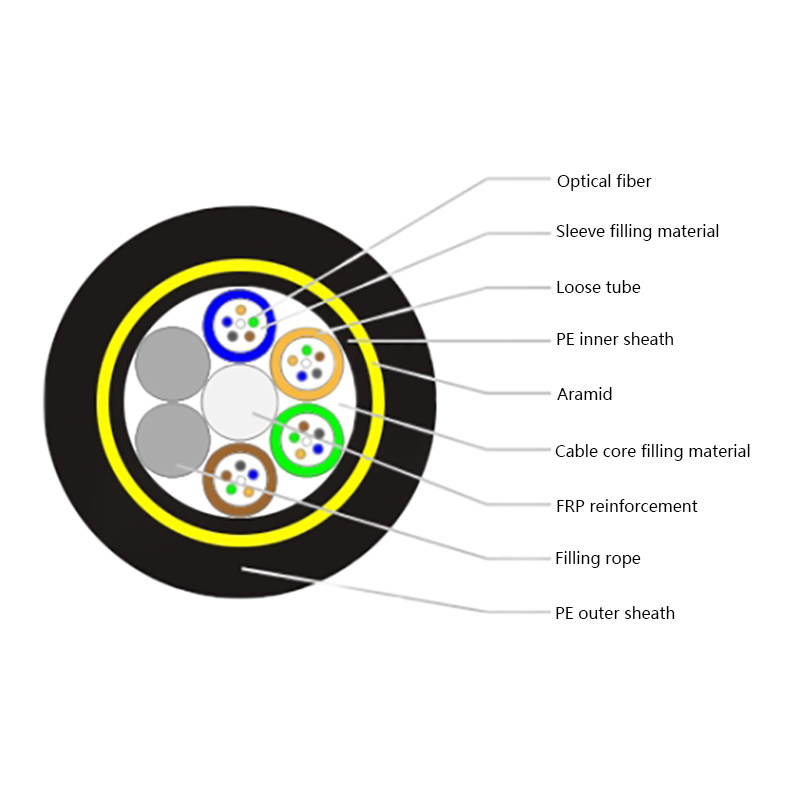
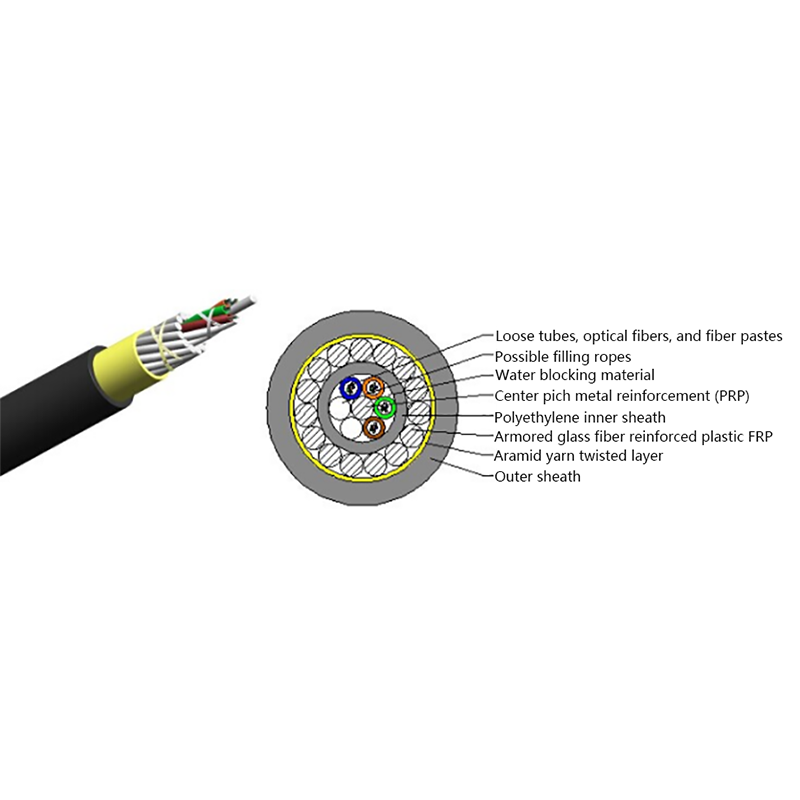
Core Design Characteristics of Micro Cables
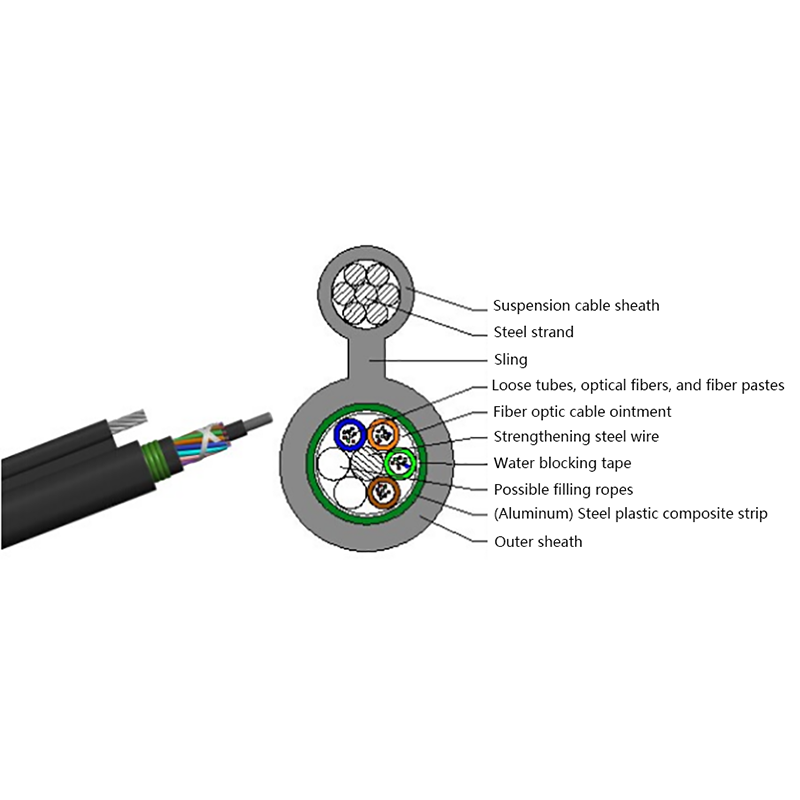
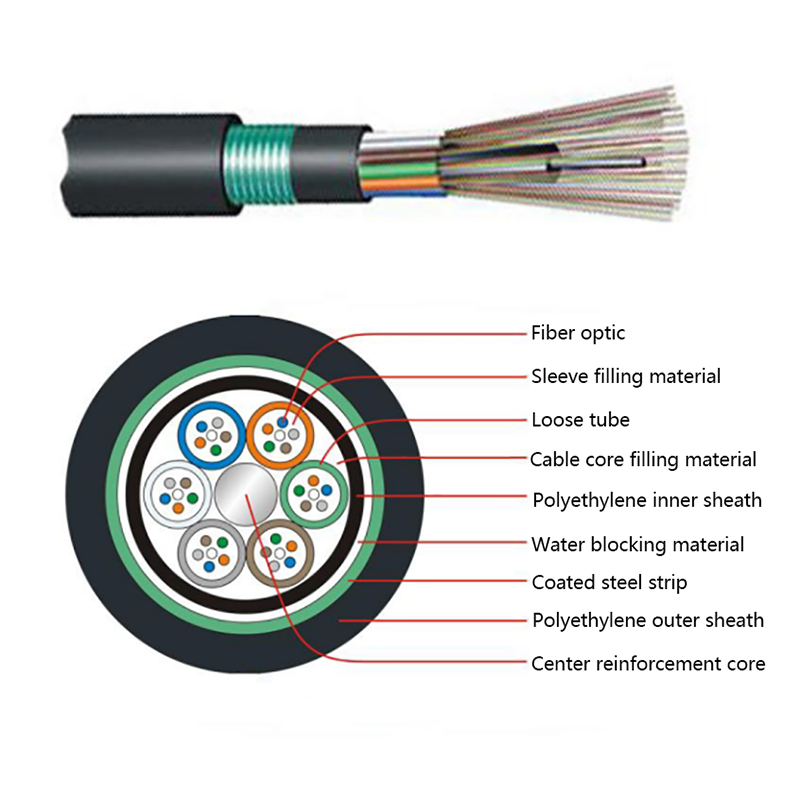
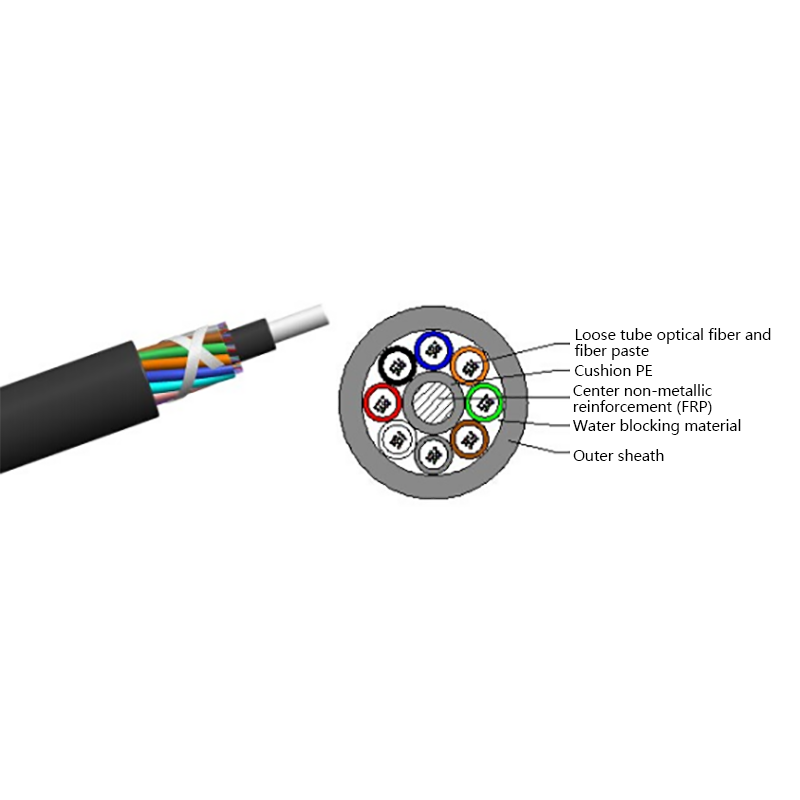
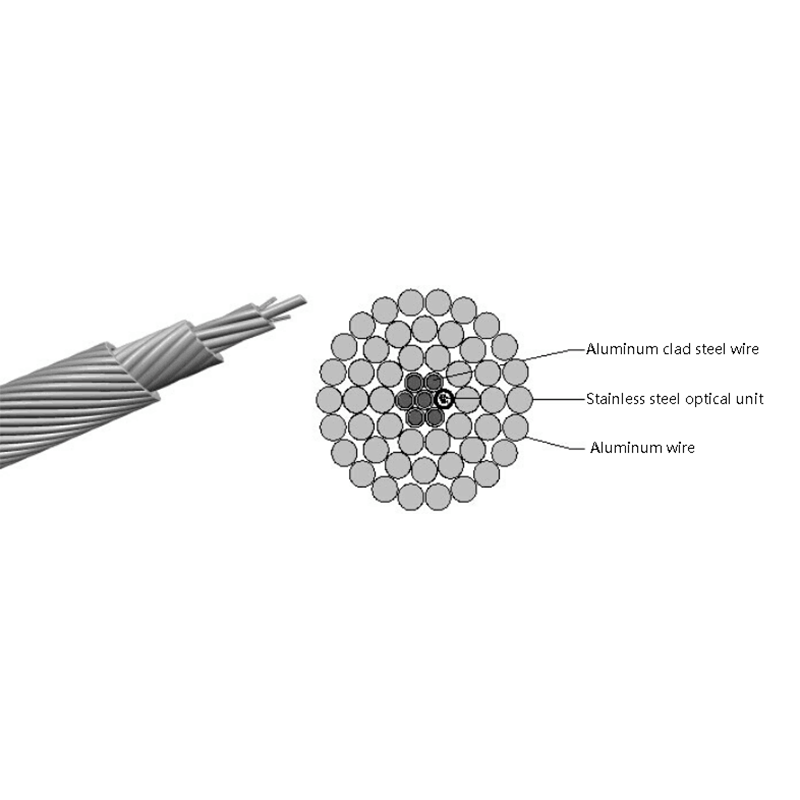
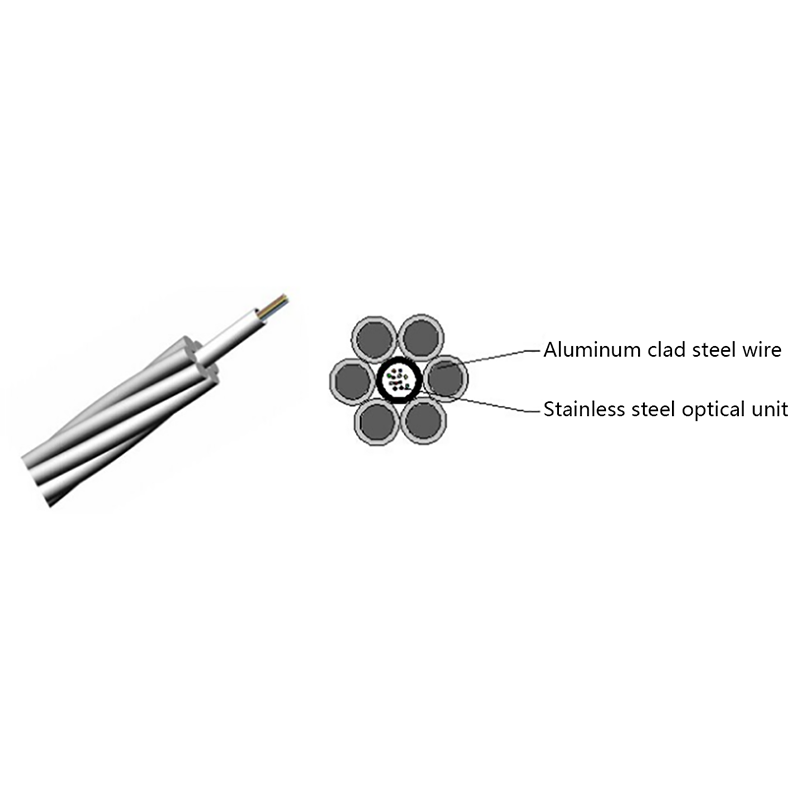
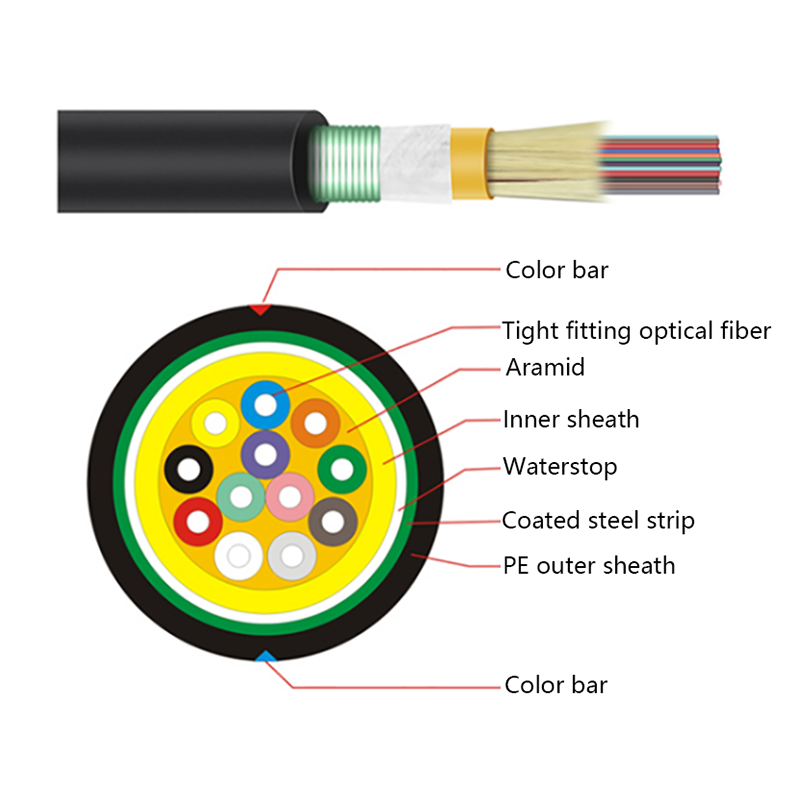
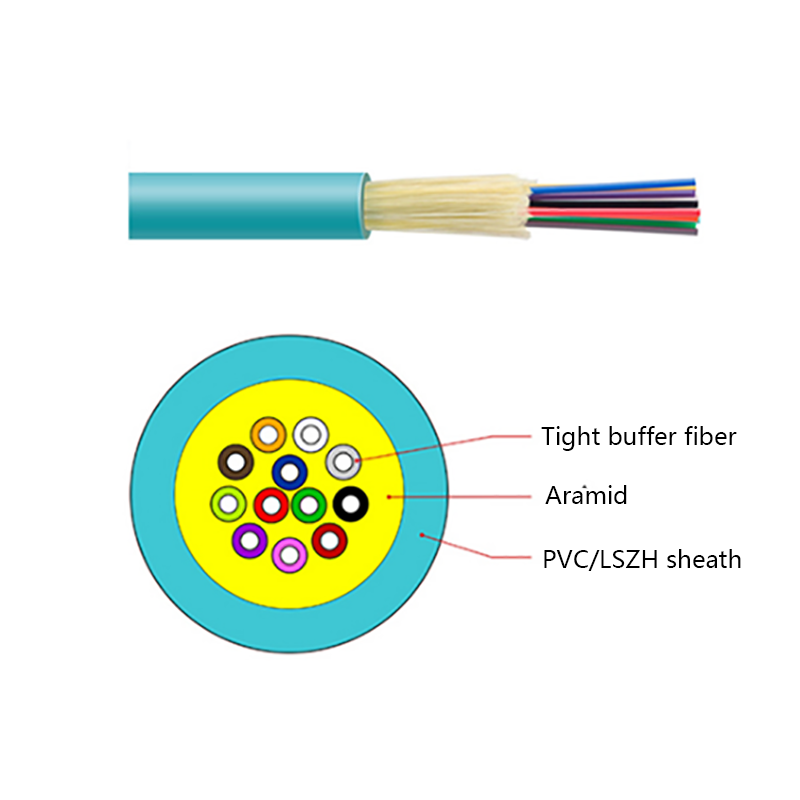
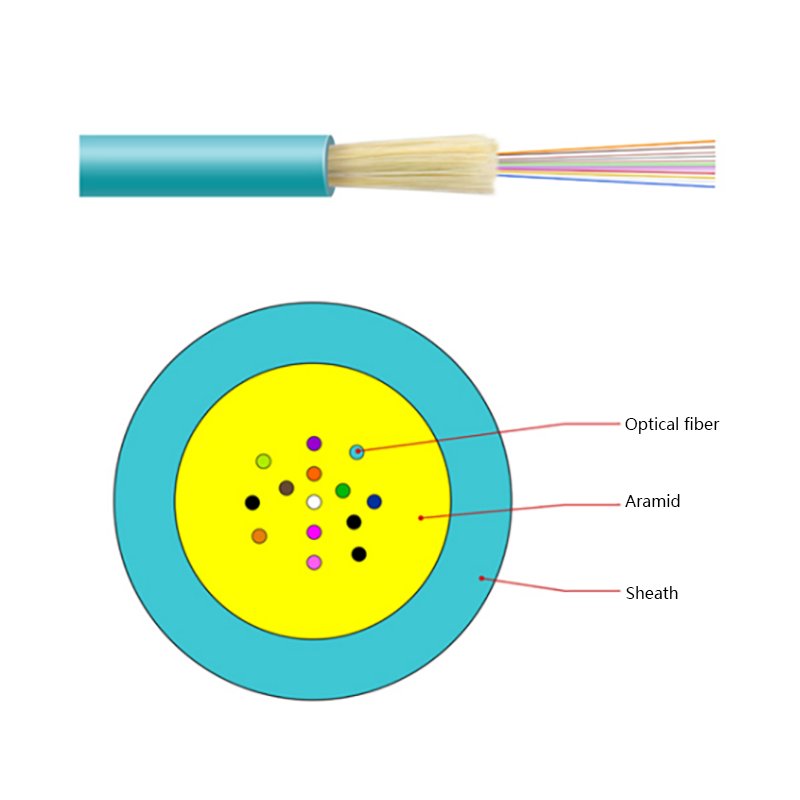
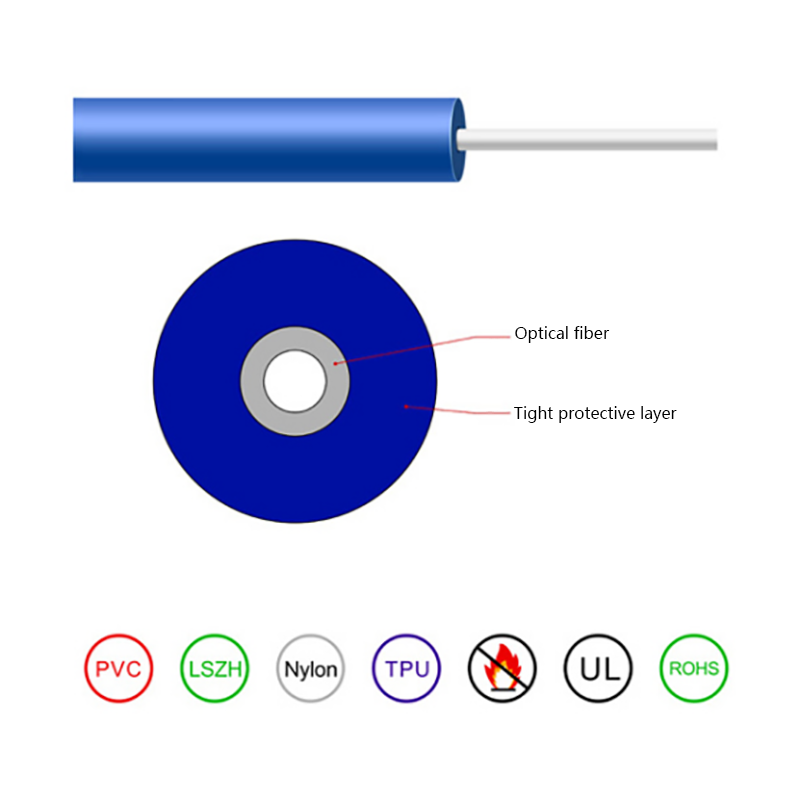
Micro cables differ from conventional fiber optic cables in both structure and materials. Their compact design is optimized for airflow efficiency, flexibility, and durability within narrow ducts.
- Small outer diameter, typically ranging from 1.5 mm to 6 mm
- Smooth or low-friction sheath to improve blowing performance
- Central or stranded fiber units with optimized fiber excess length
- Minimal or no metallic elements, reducing weight and stiffness
These characteristics allow micro cables to navigate bends and long duct routes while maintaining installation efficiency and long-term reliability.
Microduct Compatibility and System Design
Air blown micro cables are not standalone products; they are part of a complete microduct system. Proper compatibility between cable diameter and duct inner diameter is critical. Oversized cables reduce blowing distance, while undersized cables may lead to instability during installation.
Typical Cable-to-Duct Ratios
| Microduct Inner Diameter | Recommended Cable Diameter |
| 3.5 mm | 2.0–2.5 mm |
| 5.0 mm | 3.0–3.5 mm |
| 7.0 mm | 4.0–5.0 mm |
System designers must also consider duct material, inner surface quality, joint integrity, and allowable bend radius throughout the route.
Installation Process and Practical Considerations
The installation of air blown micro cables requires specialized blowing equipment that combines compressed air with controlled cable feeding. Preparation of the duct route is just as important as the blowing itself.
Key Installation Steps
- Cleaning and pressure testing the microduct before installation
- Selecting appropriate blowing parameters such as air pressure and feed speed
- Monitoring cable movement to prevent buckling or oscillation
- Sealing duct ends after installation to maintain long-term performance
Environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity can also influence installation distance and consistency. Proper training of technicians significantly improves success rates.
Performance Benefits Compared to Pulled Fiber
One of the strongest advantages of air blown micro cables is reduced mechanical stress. Traditional pulling methods apply continuous tensile force, which can stretch fibers and increase attenuation over time.
With air blowing, friction is dramatically reduced, enabling longer installation distances, easier mid-span access, and the ability to replace or upgrade cables without reopening ducts.
Common Deployment Scenarios
Air Blown Micro Cables are widely used in access networks, metropolitan fiber systems, and data center interconnections. Their scalability makes them particularly valuable where future expansion is uncertain.
- FTTH and FTTx last-mile deployments
- Urban micro-trenching projects
- Campus and industrial networks requiring phased growth
Maintenance, Upgrades, and Long-Term Use
A major operational benefit of micro cable systems is ease of maintenance. Cables can be removed and replaced without disturbing the duct infrastructure, allowing network upgrades with minimal disruption.
Proper documentation of duct routes, cable types, and installation parameters helps ensure smooth future expansions. When combined with quality microd



 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体