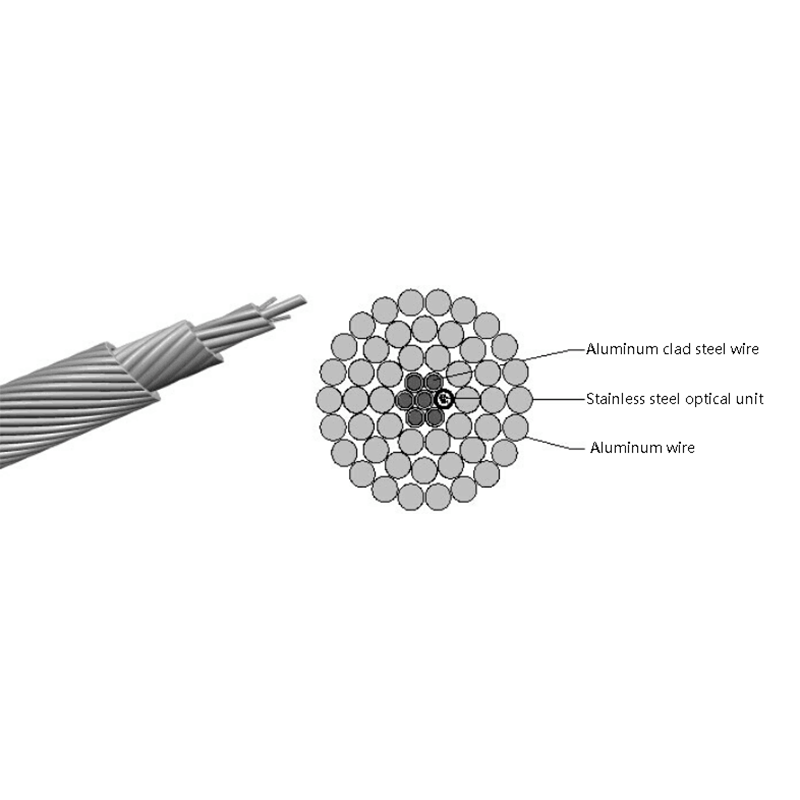
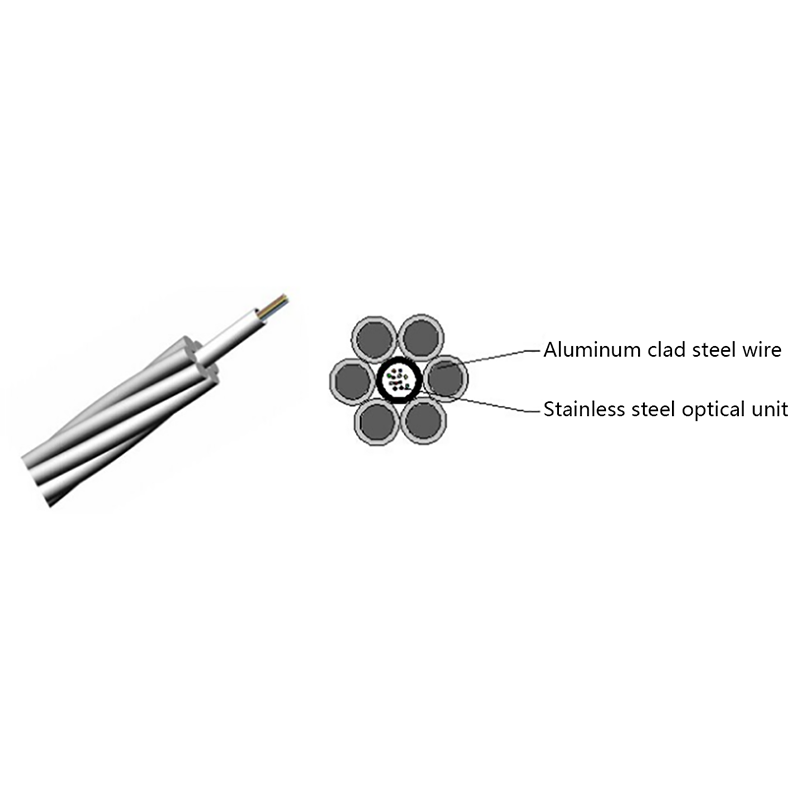
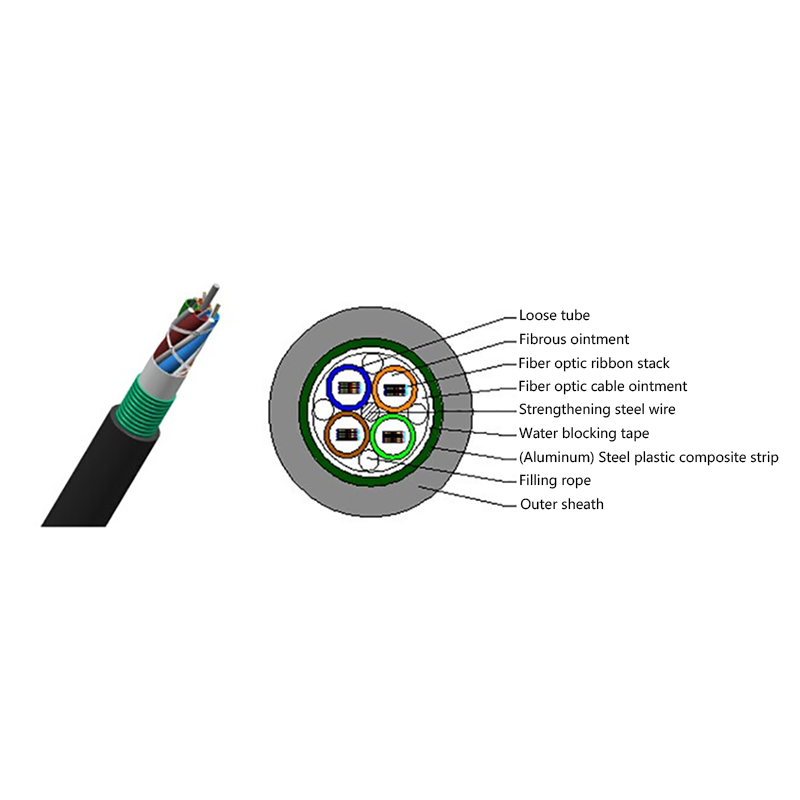
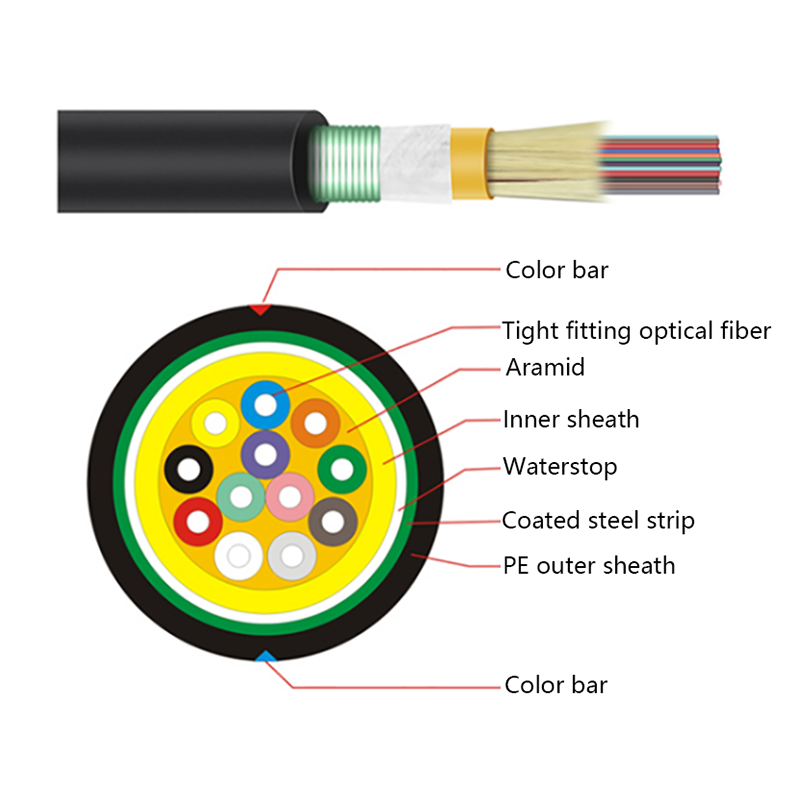
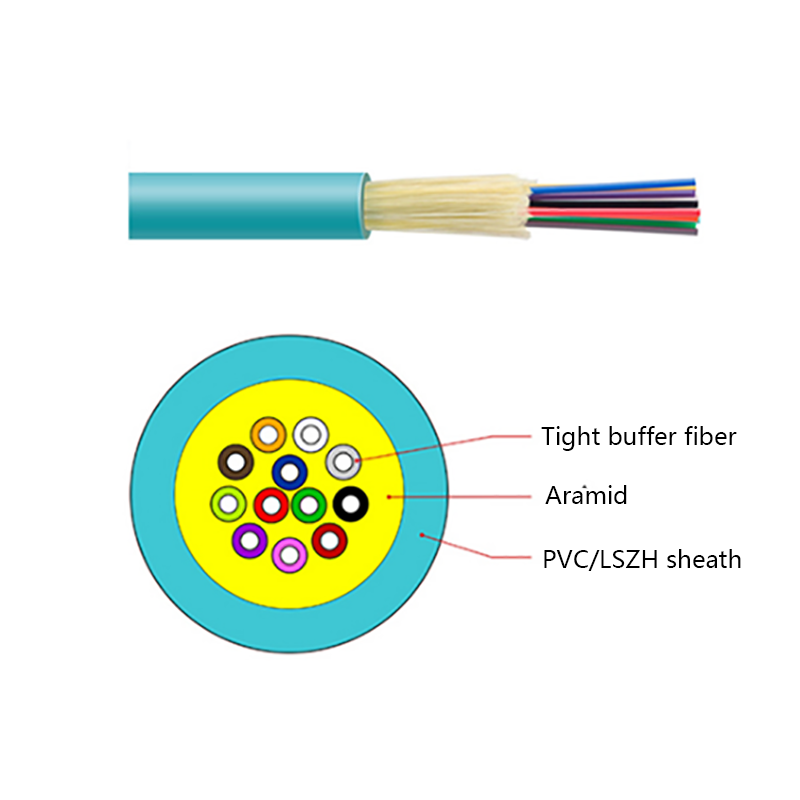
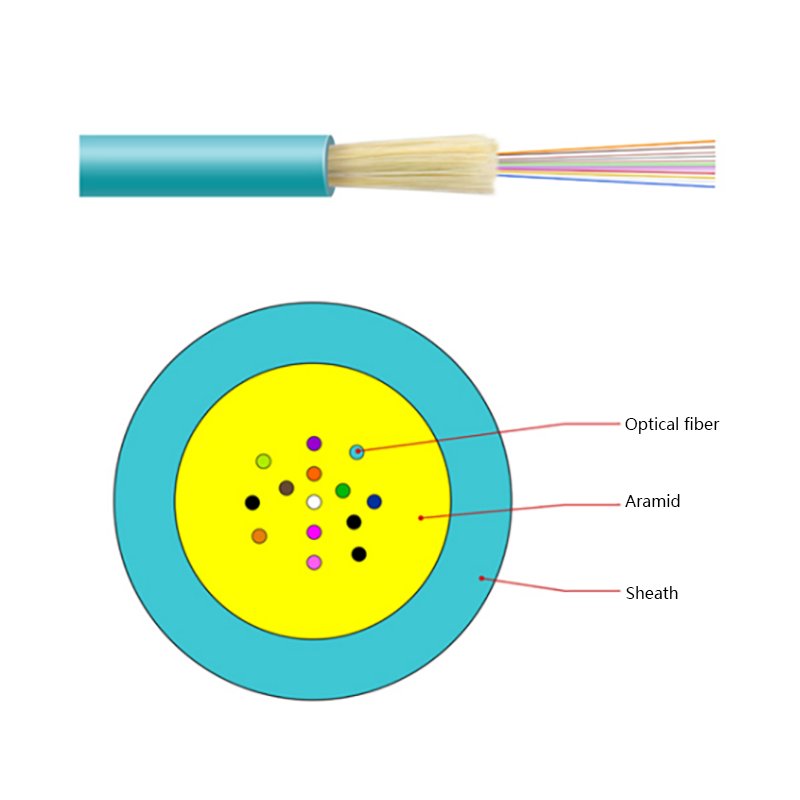
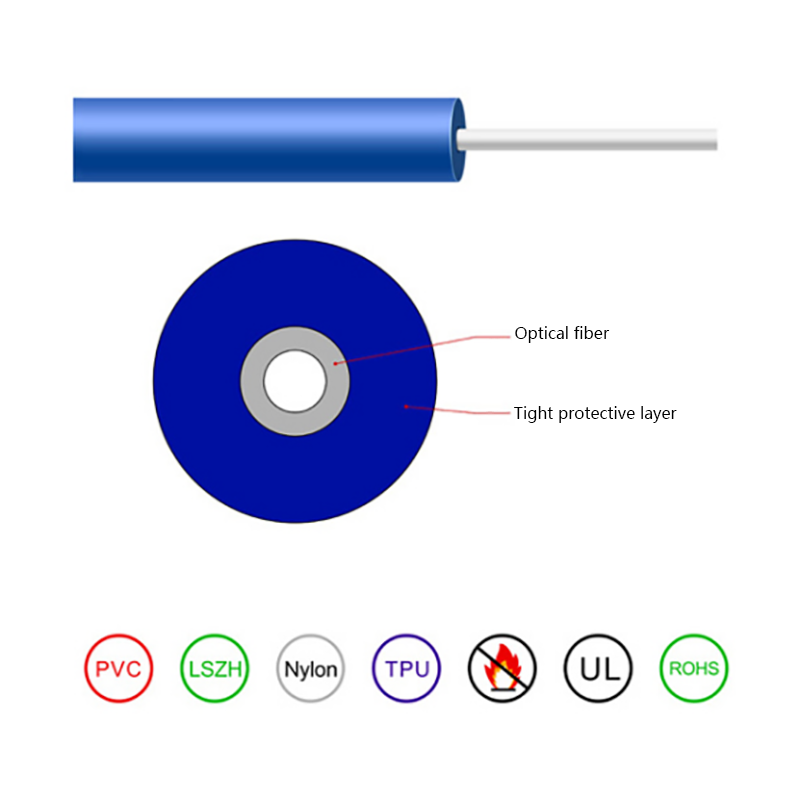
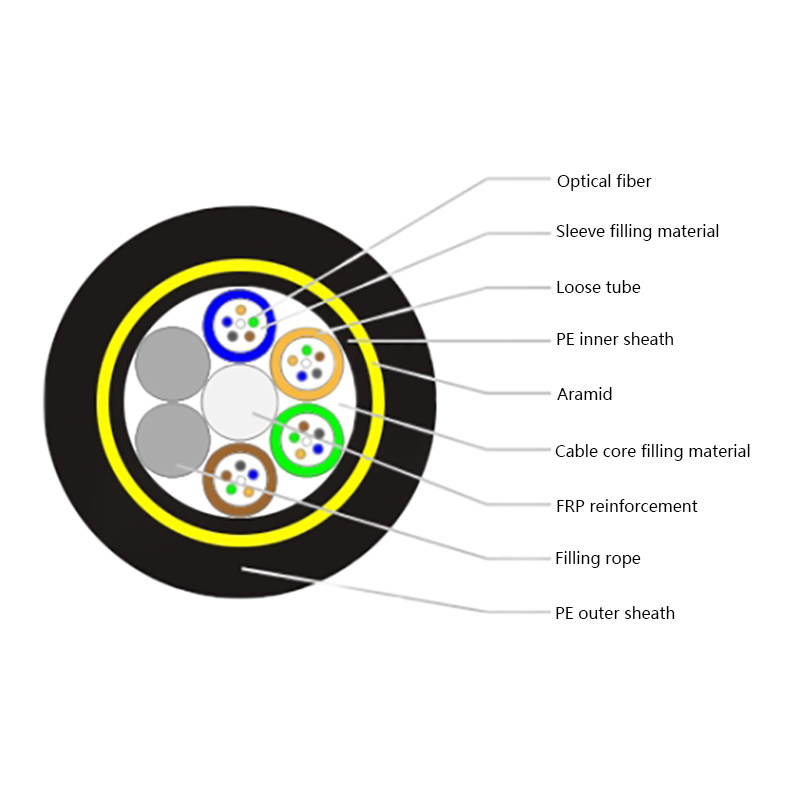
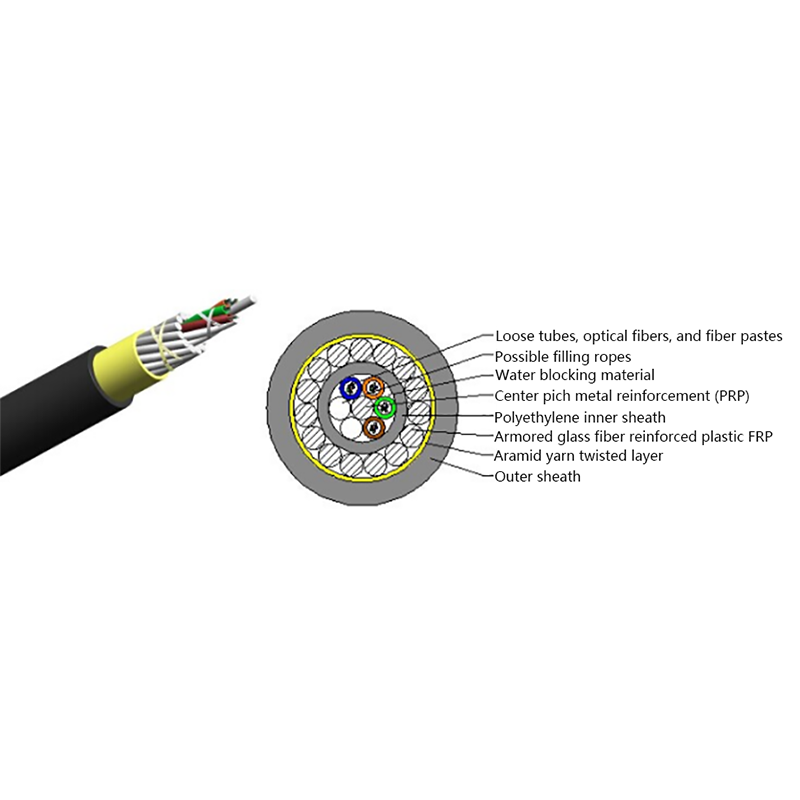
What Are the Advantages of Optical Cables Over Copper Cables?
In today’s increasingly connected world, the infrastructure that carries data has become more critical than ever. Whether it’s powering high-speed internet, supporting data centers, or enabling telecommunications, the choice of cabling technology can have a significant impact on performance, reliability, and scalability. Two of the most widely used types of data transmission cables are optical cables and copper cables. While both have their place in networks, optical cables have several distinct advantages over copper cables that make them increasingly the preferred choice in modern applications.
Understanding Optical and Copper Cables
Before diving into the advantages, it’s important to understand what these two types of cables are and how they work.
Copper Cables: Copper cables, including twisted pair and coaxial cables, transmit data through electrical signals. The flow of electrons carries information from one point to another. Copper has been the backbone of telecommunication networks for decades, largely due to its relatively low cost and widespread availability.
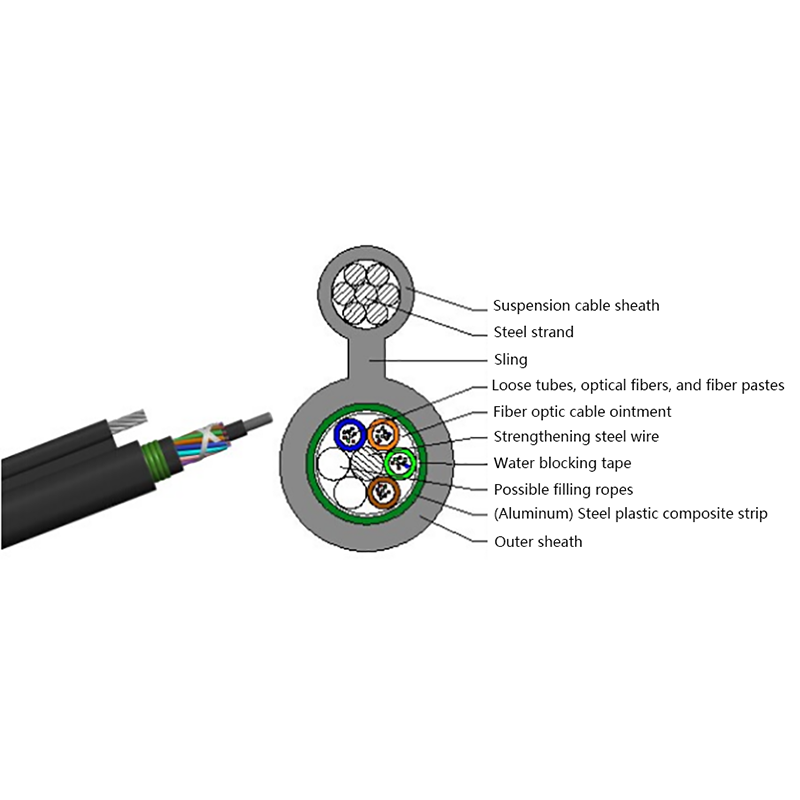
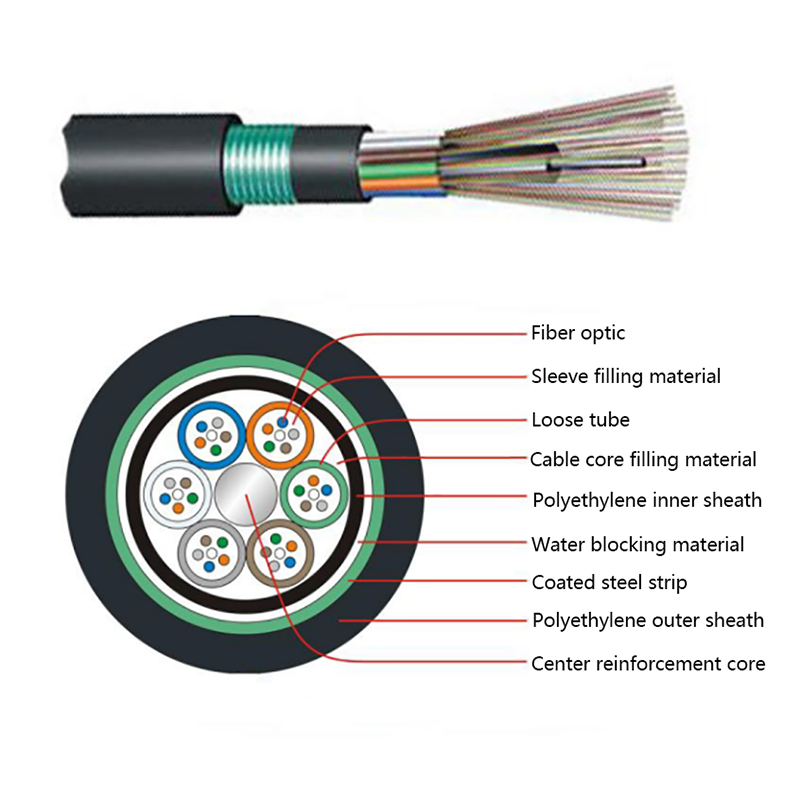
Optical Cables: Optical cables, on the other hand, transmit data as light pulses through strands of glass or plastic fibers. The technology relies on the principle of total internal reflection, allowing light to travel long distances with minimal loss of signal. Because optical cables use light rather than electricity, they offer a fundamentally different approach to data transmission.
High Bandwidth and Faster Data Transmission
One of the most significant advantages of optical cables over copper cables is bandwidth capacity. Optical fibers can carry far more data at much higher speeds than copper cables. While copper cables can handle gigabit speeds over short distances, optical cables can support terabit speeds across hundreds of kilometers.
This high bandwidth is particularly advantageous in environments that demand fast and large-scale data transmission, such as data centers, internet backbones, and cloud computing networks. Optical cables ensure that as our demand for streaming, cloud services, and real-time data grows, the infrastructure can handle it without major upgrades.
Longer Transmission Distances
Copper cables have a limited transmission distance due to signal attenuation. Over long distances, the electrical signals degrade, requiring repeaters or amplifiers to maintain signal strength. For example, standard twisted-pair copper cables are typically effective up to 100 meters without signal boosting.
Optical cables, in contrast, can transmit signals over tens to hundreds of kilometers without significant loss. Single-mode fibers, commonly used for long-haul communication, can span hundreds of kilometers before requiring signal amplification. This makes optical cables ideal for intercity or international networks where long-distance data transmission is critical.
Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference
Another critical advantage of optical cables is their resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI). Copper cables transmit electrical signals, which can be affected by nearby electrical devices, motors, or power lines. This interference can cause data loss, errors, or slower transmission speeds.
Optical cables transmit light, which is unaffected by electromagnetic fields. This makes optical cables highly reliable in industrial settings, medical facilities, and environments with heavy electrical equipment. Even in areas with high-voltage lines or strong electromagnetic sources, optical cables maintain consistent performance.
Enhanced Security
Data security is increasingly important in today’s digital landscape. Copper cables are susceptible to tapping or eavesdropping because electrical signals can be intercepted with the right tools. Optical cables offer enhanced security since intercepting a light signal in a fiber optic cable is extremely difficult without being detected.
In addition, optical cables do not radiate signals like copper cables do, reducing the risk of unintentional data leaks. This makes optical cables ideal for transmitting sensitive information, such as financial data, government communications, or private corporate networks.
Lightweight and Space-Saving
In many installations, particularly in data centers and urban infrastructure, space and weight are important considerations. Optical cables are generally thinner and lighter than copper cables, even when providing the same or greater bandwidth capacity.
A single optical cable can carry multiple channels of data simultaneously using techniques like wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM), reducing the number of cables needed for high-capacity networks. This saves space in cable trays and conduits, making installation and maintenance more manageable.
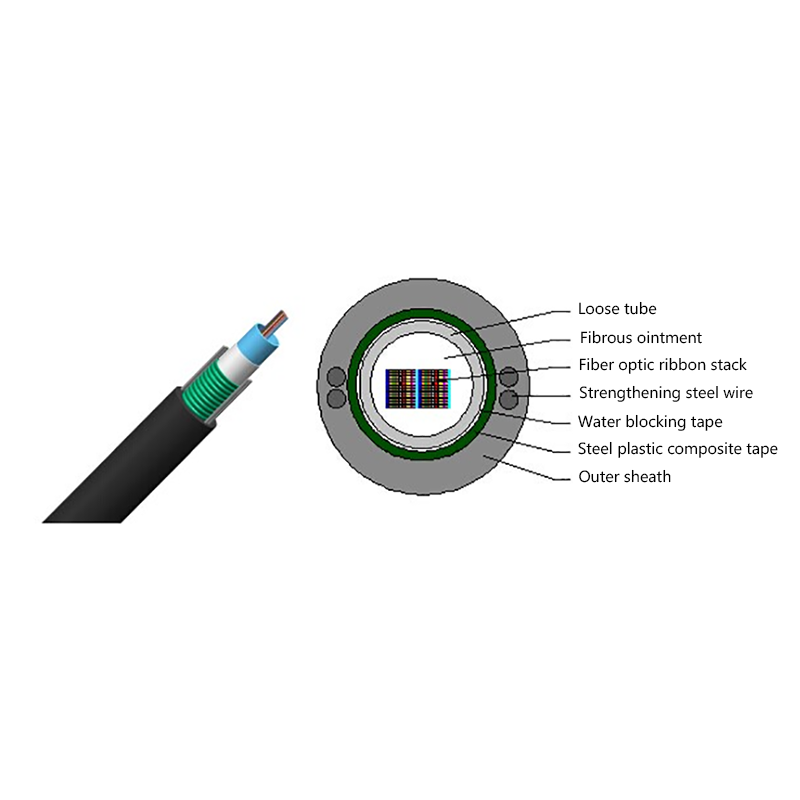
Lower Signal Loss and Energy Efficiency
Electrical signals in copper cables experience resistance, which leads to signal attenuation and heat generation. Maintaining signal strength over long distances requires repeaters or signal boosters, consuming additional energy.
Optical cables experience much lower signal loss, reducing the need for intermediate amplification in long-distance applications. This not only improves performance but also results in energy savings. For large-scale networks and data centers, this can lead to substantial reductions in operational costs over time.
Durability and Longevity
Optical cables are less prone to degradation over time compared to copper cables. They are resistant to corrosion, moisture, and chemical exposure, which are common causes of copper cable deterioration. In outdoor installations or harsh environmental conditions, optical cables maintain performance and require less frequent replacement.
Armored optical cables offer additional protection against physical damage, rodents, or accidental impacts, ensuring long-term reliability even in challenging environments.
Versatility in Applications
The advantages of optical cables make them highly versatile across multiple applications:
- Telecommunications: Optical cables are the standard for backbone networks, supporting high-speed internet and long-distance calls.
- Data Centers: Optical cables enable high-speed connections between servers, storage systems, and switches, supporting growing data demands.
- Medical and Industrial: Optical cables are immune to EMI, making them suitable for sensitive equipment and industrial automation systems.
- Submarine Communication: Undersea optical cables connect continents, transmitting massive amounts of data across oceans with minimal loss.
Copper cables, while still used in certain local area networks (LANs) and short-distance applications, cannot match this level of versatility.
Cost Considerations
Historically, copper cables were cheaper to install than optical cables. However, when considering the total cost of ownership—including maintenance, upgrades, energy usage, and network performance—optical cables often provide better long-term value. The efficiency, speed, and reliability of optical networks can outweigh the initial higher investment, particularly for enterprises, telecommunications providers, and high-demand network environments.
Environmental Benefits
Because optical cables are more energy-efficient and durable, they also offer environmental advantages. Reduced power consumption and longer service life mean fewer resources are consumed over time. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in infrastructure planning, optical cables contribute to greener networking solutions.
Conclusion
While copper cables have served as the backbone of data transmission for decades, optical cables have emerged as the superior choice for modern networking needs. With higher bandwidth, longer transmission distances, immunity to interference, enhanced security, energy efficiency, and durability, optical cables provide a future-ready solution for industries, enterprises, and governments.
As data demands continue to grow, the advantages of optical cables over copper cables become increasingly clear. Investing in optical cable infrastructure today not only ensures faster and more reliable communication but also prepares networks for the technological demands of tomorrow.



 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体